Molecular ties between the cell cycle and differentiation in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 24979803
- PMCID: PMC4084474
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1408638111
Molecular ties between the cell cycle and differentiation in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
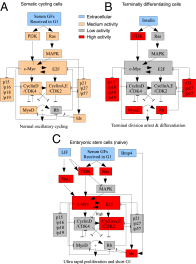
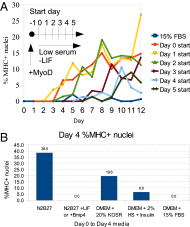
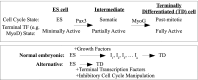
Attainment of the differentiated state during the final stages of somatic cell differentiation is closely tied to cell cycle progression. Much less is known about the role of the cell cycle at very early stages of embryonic development. Here, we show that molecular pathways involving the cell cycle can be engineered to strongly affect embryonic stem cell differentiation at early stages in vitro. Strategies based on perturbing these pathways can shorten the rate and simplify the lineage path of ES differentiation. These results make it likely that pathways involving cell proliferation intersect at various points with pathways that regulate cell lineages in embryos and demonstrate that this knowledge can be used profitably to guide the path and effectiveness of cell differentiation of pluripotent cells.
Keywords: differentiation modeling; guided differentiation; proliferation control; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Muñoz-Alonso M, León J. G1 phase control and cell differentiation. In: Boonstra J, editor. G1 Phase Progression. Georgetown, TX: Landes Bioscience; 2003. pp. 236–264.
-
- Budirahardja Y, Gönczy P. Coupling the cell cycle to development. Development. 2009;136(17):2861–2872. - PubMed
-
- Thoma EC, Maurus K, Wagner TU, Schartl M. Parallel differentiation of embryonic stem cells into different cell types by a single gene-based differentiation system. Cell Reprogram. 2012;14(2):106–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

