Evaluation of developmental toxicity of propylthiouracil and methimazole
- PMID: 24980470
- PMCID: PMC4295064
- DOI: 10.1002/bdrb.21113
Evaluation of developmental toxicity of propylthiouracil and methimazole
Abstract
Background: Propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole (MMI) are antithyroid drugs used to treat hyperthyroidism. Despite the widespread use of PTU and MMI during pregnancy, modest clinical data and less animal data are available on the teratogenic potential of these drugs.
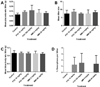
Methods: We evaluated the teratogenicity of in utero exposure to PTU or MMI in mice and rats. First, pregnant C57Bl/6 mice were treated daily with PTU (10 or 100 mg/kg), MMI (2 or 20 mg/kg), or vehicle from gestation day (GD) 6 to 16. GD 18 fetuses were evaluated for gross and histopathological abnormalities. Next, pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats were treated daily with PTU (50 or 100 mg/kg), MMI (10 or 20 mg/kg), or vehicle from GD 6 to 19, followed by evaluation for gross and histopathological abnormalities at GD 20.
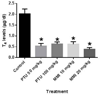
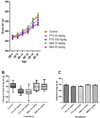
Results: In mice treated with PTU or MMI, no significant histopathological abnormalities or external gross malformations, and no adverse effects on placental weight, litter size, resorption rates, or fetal weight were observed at GD 18. In rats, no adverse effects on litter size, placental weights, or maternal body weights were observed with either PTU or MMI treatment. PTU treatment (50 and 100 mg/kg) and MMI (10 mg/kg) treatment resulted in a decrease in crown-rump length in rat fetuses but no external gross malformations or histopathological abnormalities were observed.
Conclusion: We did not observe either gross external malformations or histopathological malformations in mice or rats treated long-term with high doses of PTU or MMI during pregnancy.
Keywords: antithyroid drugs; developmental toxicity; methimazole; propylthiouracil.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Abalovich M, Amino N, Barbour LA, Cobin RH, De Groot LJ, Glinoer D, Mandel SJ, Stagnaro-Green A. Management of thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy and postpartum: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8 Suppl):S1–S47. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SL, Olsen J, Wu CS, Laurberg P. Birth defects after early pregnancy use of antithyroid drugs: A danish nationwide study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(11):4373–4381. - PubMed
-
- Bahn RS, Burch HS, Cooper DS, Garber JR, Greenlee CM, Klein IL, Laurberg P, McDougall IR, Rivkees SA, Ross D, Sosa JA, Stan MN. The role of propylthiouracil in the management of graves' disease in adults: Report of a meeting jointly sponsored by the american thyroid association and the food and drug administration. Thyroid. 2009;19(7):673–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

