An introduction to the analysis of shotgun metagenomic data
- PMID: 24982662
- PMCID: PMC4059276
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00209
An introduction to the analysis of shotgun metagenomic data
Abstract
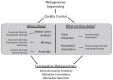
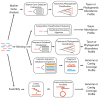
Environmental DNA sequencing has revealed the expansive biodiversity of microorganisms and clarified the relationship between host-associated microbial communities and host phenotype. Shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing is a relatively new and powerful environmental sequencing approach that provides insight into community biodiversity and function. But, the analysis of metagenomic sequences is complicated due to the complex structure of the data. Fortunately, new tools and data resources have been developed to circumvent these complexities and allow researchers to determine which microbes are present in the community and what they might be doing. This review describes the analytical strategies and specific tools that can be applied to metagenomic data and the considerations and caveats associated with their use. Specifically, it documents how metagenomes can be analyzed to quantify community structure and diversity, assemble novel genomes, identify new taxa and genes, and determine which metabolic pathways are encoded in the community. It also discusses several methods that can be used compare metagenomes to identify taxa and functions that differentiate communities.
Keywords: bioinformatics; host–microbe interactions; metagenome; microbial diversity; microbiome; microbiota; review.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

