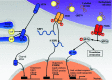
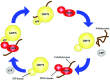
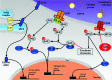
Role of p58IPK in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-associated Apoptosis and Inflammation
- PMID: 24982747
- PMCID: PMC4074489
Role of p58IPK in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-associated Apoptosis and Inflammation
Figures

References
-
- Yoshida H. ER stress and diseases. FEBS J. 2007;274:630–658. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Kaufman RJ. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:374. - PubMed
-
- Calnexin, calreticulin and the folding of glycoproteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7:193–200. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
