Effectiveness of combined high-dosed trospium and solifenacin depending on severity of OAB symptoms in elderly men and women under cyclic therapy
- PMID: 24982780
- PMCID: PMC4074719
- DOI: 10.5173/ceju.2014.01.art9
Effectiveness of combined high-dosed trospium and solifenacin depending on severity of OAB symptoms in elderly men and women under cyclic therapy
Abstract
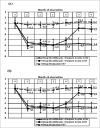
Material and methods: 313 patients, 196 women and 117 men over 65 (average age 68.6) were included in this study. All patients underwent urodynamic examination before enrollment and after the study was completed. For clinical evaluation of LUT state ICIQ-SF questionnaires and bladder diaries were used. Patients with moderate (А, n = 155) and severe (В, n = 158) symptoms of OAB. Each group was divided into subgroups in which patients received Trospium 60 mg/day and Solifenacin 20 mg/day during two cycles - 1.5 and 1 month with one month interval (А1 and В1); subgroups in which second cycle was substituted with placebo (А2, В2), and control groups (А3, В3).
Results: In groups with moderate symptoms of OAB ratio of patients demonstrated decrease of frequency of EI ≥1.5 a day remained at the level of 45-60% during all observation period. In subgroups with severe symptoms of OAB percentage of such patients was 55.3% for the subgroup which received two cycle therapy, and decreased to 26% in the subgroup which underwent 1 cycle therapy. Urodynamic indices for state of LUT correlated with clinical indicators (r =0.57-0.71 at p≤ 0.05).
Conclusions: Short single cycle of high-dosed Solifenacin and Trospium in elderly patients with moderate symptoms of OAB enables to maintain long therapeutic effect with acceptable level of side effects. This treatment algorithm applied in two cycle course is an effective and safe method for management of severe symptoms of OAB in elderly patients without increased risk of side effects.
Keywords: antimuscarinic; elderly; overactive bladder.
Figures



References
-
- Milsom I, Coyne KS, Nicholson S, Kvasz M, Chen CI, Wein AJ. Global Prevalence and Economic Burden of Urgency Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review. Eur Urol. 2013;65:79–95. - PubMed
-
- Ruffion A, Castro–Diaz D, Patel H, Khalaf K, Onyenwenyi A, Globe D, et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology of urinary incontinence and detrusor overactivity among patients with neurogenic overactive bladder. Neuroepidemiology. 2013;41:146–155. - PubMed
-
- Milsom I, Stewart W, Thuroff J. The prevalence of overactive bladder. Am J Manag Care. 2000;6(Suppl):S565–573. - PubMed
-
- Rantell A. Assessment and diagnosis of overactive bladder in women. Nurs Stand. 2013;27:35–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
