A population-based investigation into the self-reported reasons for sleep problems
- PMID: 24983754
- PMCID: PMC4077805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101368
A population-based investigation into the self-reported reasons for sleep problems
Abstract
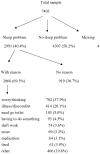
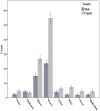
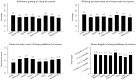
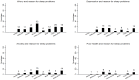
Typologies of sleep problems have usually relied on identifying underlying causes or symptom clusters. In this study the value of using the patient's own reasons for sleep disturbance are explored. Using secondary data analysis of a nationally representative psychiatric survey the patterning of the various reasons respondents provided for self-reported sleep problems were examined. Over two thirds (69.3%) of respondents could identify a specific reason for their sleep problem with worry (37.9%) and illness (20.1%) representing the most commonly reported reasons. And while women reported more sleep problems for almost every reason compared with men, the patterning of reasons by age showed marked variability. Sleep problem symptoms such as difficulty getting to sleep or waking early also showed variability by different reasons as did the association with major correlates such as worry, depression, anxiety and poor health. While prevalence surveys of 'insomnia' or 'poor sleep' often assume the identification of an underlying homogeneous construct there may be grounds for recognising the existence of different sleep problem types particularly in the context of the patient's perceived reason for the problem.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ohayon MM (2002) Epidemiology of insomnia: what we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Med Rev 6: 97–111. - PubMed
-
- Dregan A, Armstrong D (2011) Cross-country variation in sleep disturbance among working and older age groups: an analysis based on the European Social Survey. Int Psychogeriatr 23: 1413–1420. - PubMed
-
- Hislop JA, Arber S (2006) Sleep, gender and ageing: temporal perspectives in the mid-to-later life transition. In: Calasanti TS, K., editor. Age matters: Realigning feminist thinking. New York: Routledge. pp. 225–246.
-
- Morgan K, Dallosso H, Ebrahim S, Arie T, Fentem PH (1988) Characteristics of subjective insomnia in the elderly living at home. Age Ageing 17: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Dregan A, Armstrong D (2009) Age, cohort and period effects in the prevalence of sleep disturbances among older people: the impact of economic downturn. Soc Sci Med 69: 1432–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

