Comparative validation of the D. melanogaster modENCODE transcriptome annotation
- PMID: 24985915
- PMCID: PMC4079975
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.159384.113
Comparative validation of the D. melanogaster modENCODE transcriptome annotation
Abstract
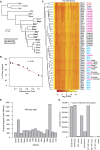
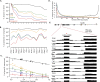
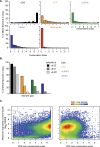
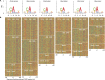
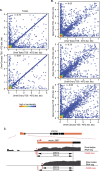
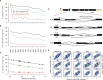
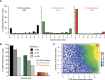
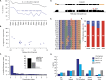
Accurate gene model annotation of reference genomes is critical for making them useful. The modENCODE project has improved the D. melanogaster genome annotation by using deep and diverse high-throughput data. Since transcriptional activity that has been evolutionarily conserved is likely to have an advantageous function, we have performed large-scale interspecific comparisons to increase confidence in predicted annotations. To support comparative genomics, we filled in divergence gaps in the Drosophila phylogeny by generating draft genomes for eight new species. For comparative transcriptome analysis, we generated mRNA expression profiles on 81 samples from multiple tissues and developmental stages of 15 Drosophila species, and we performed cap analysis of gene expression in D. melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura. We also describe conservation of four distinct core promoter structures composed of combinations of elements at three positions. Overall, each type of genomic feature shows a characteristic divergence rate relative to neutral models, highlighting the value of multispecies alignment in annotating a target genome that should prove useful in the annotation of other high priority genomes, especially human and other mammalian genomes that are rich in noncoding sequences. We report that the vast majority of elements in the annotation are evolutionarily conserved, indicating that the annotation will be an important springboard for functional genetic testing by the Drosophila community.
© 2014 Chen et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195 - PubMed
-
- Balakirev ES, Ayala FJ 2003. Pseudogenes: are they “junk” or functional DNA? Annu Rev Genet 37: 123–151 - PubMed
-
- Banerji J, Olson L, Schaffner W 1983. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell 33: 729–740 - PubMed
-
- Bass B, Hundley H, Li JB, Peng Z, Pickrell J, Xiao XG, Yang L 2012. The difficult calls in RNA editing. Nat Biotechnol 30: 1207–1209 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
