Wave-CAIPI for highly accelerated 3D imaging
- PMID: 24986223
- PMCID: PMC4281518
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25347
Wave-CAIPI for highly accelerated 3D imaging
Abstract
Purpose: To introduce the wave-CAIPI (controlled aliasing in parallel imaging) acquisition and reconstruction technique for highly accelerated 3D imaging with negligible g-factor and artifact penalties.
Methods: The wave-CAIPI 3D acquisition involves playing sinusoidal gy and gz gradients during the readout of each kx encoding line while modifying the 3D phase encoding strategy to incur interslice shifts as in 2D-CAIPI acquisitions. The resulting acquisition spreads the aliasing evenly in all spatial directions, thereby taking full advantage of 3D coil sensitivity distribution. By expressing the voxel spreading effect as a convolution in image space, an efficient reconstruction scheme that does not require data gridding is proposed. Rapid acquisition and high-quality image reconstruction with wave-CAIPI is demonstrated for high-resolution magnitude and phase imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping.
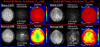
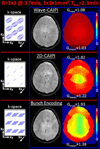
Results: Wave-CAIPI enables full-brain gradient echo acquisition at 1 mm isotropic voxel size and R = 3 × 3 acceleration with maximum g-factors of 1.08 at 3T and 1.05 at 7T. Relative to the other advanced Cartesian encoding strategies (2D-CAIPI and bunched phase encoding) wave-CAIPI yields up to two-fold reduction in maximum g-factor for nine-fold acceleration at both field strengths.
Conclusion: Wave-CAIPI allows highly accelerated 3D acquisitions with low artifact and negligible g-factor penalties, and may facilitate clinical application of high-resolution volumetric imaging.
Keywords: CAIPIRINHA, quantitative susceptibility mapping; parallel imaging; phase imaging.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
GRAPPA reconstructed wave-CAIPI MP-RAGE at 7 Tesla.Magn Reson Med. 2018 Dec;80(6):2427-2438. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27215. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Magn Reson Med. 2018. PMID: 29663507
-
Highly accelerated EPI with wave encoding and multi-shot simultaneous multislice imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2022 Sep;88(3):1180-1197. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29291. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Magn Reson Med. 2022. PMID: 35678236
-
Wave-CAIPI for highly accelerated MP-RAGE imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2018 Jan;79(1):401-406. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26649. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Magn Reson Med. 2018. PMID: 28220617 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid brain MRI acquisition techniques at ultra-high fields.NMR Biomed. 2016 Sep;29(9):1198-221. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3478. Epub 2016 Feb 2. NMR Biomed. 2016. PMID: 26835884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in parallel imaging for MRI.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017 Aug;101:71-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 2. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 28844222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-step quantitative susceptibility mapping with variational penalties.NMR Biomed. 2017 Apr;30(4):10.1002/nbm.3570. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3570. Epub 2016 Jun 22. NMR Biomed. 2017. PMID: 27332141 Free PMC article.
-
Motion robust magnetic resonance imaging via efficient Fourier aggregation.Med Image Anal. 2023 Jan;83:102638. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102638. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Med Image Anal. 2023. PMID: 36257133 Free PMC article.
-
Wave-LORAKS: Combining wave encoding with structured low-rank matrix modeling for more highly accelerated 3D imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Mar;81(3):1620-1633. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27511. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30252157 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced MRI quantification of neuroinflammatory disorders.J Neurosci Res. 2022 Jul;100(7):1389-1394. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25054. Epub 2022 Apr 23. J Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 35460291 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mesoscale Brain Mapping: Bridging Scales and Modalities in Neuroimaging - A Symposium Review.Neuroinformatics. 2024 Oct;22(4):679-706. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09686-2. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Neuroinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39312131 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sodickson D, Manning W. Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997 - PubMed
-
- Pruessmann K, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999;42.5:952–962. - PubMed
-
- Griswold M, Jakob P, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA) Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2002;47.6:1202–1210. - PubMed
-
- Larkman D, Hajnal J, Herlihy AH, Coutts GA, Young IR, Ehnholm G. Use of multicoil arrays for separation of signal from multiple slices simultaneously excited. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2001;13:313–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

