Interleukin-6 and procalcitonin as biomarkers in mortality prediction of hospitalized patients with community acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 24987476
- PMCID: PMC4073574
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.134072
Interleukin-6 and procalcitonin as biomarkers in mortality prediction of hospitalized patients with community acquired pneumonia
Abstract
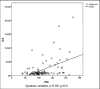
Introduction: Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) may present as life-threatening infection with uncertain progression and outcome of treatment. Primary aim of the trial was determination of the cut-off value of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and procalcitonin (PCT) above which, 30-day mortality in hospitalized patients with CAP, could be predicted with high sensitivity and specificity. We investigated correlation between serum levels of IL-6 and PCT at admission and available scoring systems of CAP (pneumonia severity index-PSI, modified early warning score-MEWS and (Confusion, Urea nitrogen, respiratory rate, Blood pressure, ≥65 years of age-CURB65).
Methods: This was prospective, non-randomized trial which included 101 patients with diagnosed CAP. PSI, MEWS and CURB65 were assessed on first day of hospitalization. IL-6 and PCT were also sampled on the first day of hospitalization.
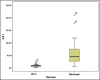
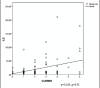
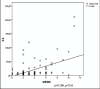
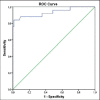
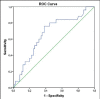
Results: Based on ROC curve analysis (AUC ± SE = 0.934 ± 0.035; 95%CI(0.864-1.0); P = 0.000) hospitalized CAP patients with elevated IL-6 level have 93.4% higher risk level for lethal outcome. Cut-off value of 20.2 pg/ml IL-6 shows sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 87% in mortality prediction. ROC curve analysis confirmed significant role of procalcitonin as a mortality predictor in CAP patients (AUC ± SE = 0.667 ± 0.062; 95%CI(0.546-0.789); P = 0.012). Patients with elevated PCT level have 66.7% higher risk level for lethal outcome. As a predictor of mortality at the cut-off value of 2.56 ng/ml PCT shows sensitivity of 76% and specificity of 61.8%.
Conclusions: Both IL-6 and PCI are significant for prediction of 30-day mortality in hospitalized patients with CAP. Serum levels of IL6 correlate with major CAP scoring systems.
Keywords: Community acquired pneumonia; interleukin-6; mortality; procalcitonin; risk assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kolditz M, Ewig S, Höffken G. Management-based risk prediction in community-acquired pneumonia by scores and biomarkers. Eur Respir J. 2013;41:974–84. - PubMed
-
- Ewig S, Torres A. Community-acquired pneumonia as an emergency: Time for an aggressive intervention to lower mortality. Eur Respir J. 2011;38:253–60. - PubMed
-
- Menéndez R, Martínez R, Reyes S, Mensa J, Filella X, Marcos MA, et al. Biomarkers improve mortality prediction by prognostic scales in community-acquired pneumonia. Thorax. 2009;64:587–91. - PubMed
-
- Ewig S, Bauer T, Richter K, Szenscenyi J, Heller G, Strauss R, et al. Prediction of in-hospital death from community-acquired pneumonia by varying CRB-age groups. Eur Respir J. 2013;41:917–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

