Effect of dietary n - 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on oxidant/antioxidant status in macrosomic offspring of diabetic rats
- PMID: 24987679
- PMCID: PMC4060321
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/368107
Effect of dietary n - 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on oxidant/antioxidant status in macrosomic offspring of diabetic rats
Abstract
The aim of this work was to determine the effect of dietary n - 3 PUFA on oxidant/antioxidant status, in vitro very low and low density lipoprotein (VLDL-LDL), and VLDL-LDL-fatty acid composition in macrosomic pups of diabetic mothers. We hypothesized that n - 3 PUFA would improve oxidative stress in macrosomia. Diabetes was induced in female Wistar rats fed with the ISIO diet (control) or with the EPAX diet (enriched in n - 3 PUFAs), by streptozotocin. The macrosomic pups were killed at birth (day 0) and at adulthood (day 90). Lipid parameters and VLDL-LDL-fatty acid composition were investigated. The oxidant/antioxidant status was determined by measuring plasma oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC), hydroperoxides, carbonyl proteins, and VLDL-LDL oxidation. Macrosomic rats of ISIO fed diabetic mothers showed an increase in plasma and VLDL-LDL-triglycerides and VLDL-LDL-cholesterol levels and altered VLDL-LDL-fatty acid composition. Plasma ORAC was low with high hydroperoxide and carbonyl protein levels. The in vitro oxidizability of VLDL-LDL was enhanced in these macrosomic rats. The EPAX diet corrected lipid parameters and improved oxidant/antioxidant status but increased VLDL-LDL susceptibility to oxidation. Macrosomia is associated with lipid abnormalities and oxidative stress. n - 3 PUFA exerts favorable effects on lipid metabolism and on the oxidant/antioxidant status of macrosomic rats. However, there are no evident effects on VLDL-LDL oxidation.
Figures
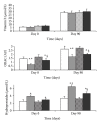
References
-
- Martin-Gronert MS, Ozanne SE. Maternal nutrition during pregnancy and health of the offspring. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2006;34(5):779–782. - PubMed
-
- Merzouk H, Madani S, Boualga A, Prost J, Bouchenak M, Belleville J. Age-related changes in cholesterol metabolism in macrosomic offspring of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Journal of Lipid Research. 2001;42(7):1152–1159. - PubMed
-
- Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Bastard JP, Jaudon MC, Delattre J. Consequences of the diabetic status on the oxidant/antioxidant balance. Diabetes and Metabolism. 2000;26(3):163–176. - PubMed
-
- Merzouk S, Hichami A, Sari A, et al. Impaired oxidant/antioxidant status and LDL-fatty acid composition are associated with increased susceptibility to peroxidation of LDL in diabetic patients. General Physiology and Biophysics. 2004;23(4):387–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

