Function and regulation of the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio
- PMID: 24987837
- PMCID: PMC4114922
- DOI: 10.4161/sgtp.29769
Function and regulation of the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio
Abstract
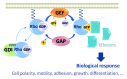
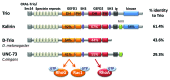
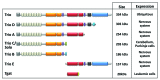
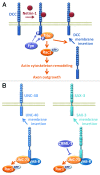
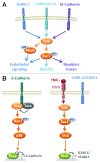
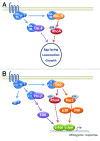
Rho GTPases oscillate between an inactive GDP-bound state and an active GTP-bound state. They are activated by Rho Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factors (GEF), which accelerate the GDP to GTP exchange. RhoGEFs fall into two different classes: the Dbl family and the DOCK family of proteins. In this review, we focus on the function and regulation of the Dbl family RhoGEF Trio. Trio and its paralog Kalirin are unique within this family in that they display two GEF domains of distinct specificity. Trio is a major regulator of neuronal development, and its function is conserved through evolution. Moreover, Trio plays an important role in cell adhesion and in signaling pathways elicited by Gαq protein-coupled receptors. Combined, these observations suggest that Trio has a major role in cellular physiology. Of note, Trio is an essential gene for mouse development, with a prominent role in the development of the nervous system. Finally, Trio expression is significantly increased in different types of tumors and it has been proposed that it could participate in oncogenesis.
Keywords: GEF; GEF inhibitors; Rho GTPases; Trio; UNC-73; actin cytoskeleton remodeling; cancer; cell adhesion; migration and invasion; neuronal differentiation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
