Sensitive and specific PCR systems for detection of both Chinese and Japanese severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains and prediction of patient survival based on viral load
- PMID: 24989600
- PMCID: PMC4313158
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00742-14
Sensitive and specific PCR systems for detection of both Chinese and Japanese severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains and prediction of patient survival based on viral load
Abstract
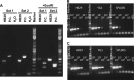
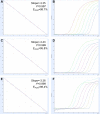
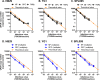
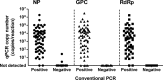
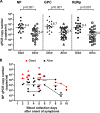
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging infectious disease with a high case fatality risk and is caused by the SFTS virus (SFTSV). A retrospective study conducted after the first identification of an SFTS patient in Japan revealed that SFTS is endemic to the region, and the virus exists indigenously in Japan. Since the nucleotide sequence of Japanese SFTSV strains contains considerable differences compared with that of Chinese strains, there is an urgent need to establish a sensitive and specific method capable of detecting the Chinese and Japanese strains of SFTSV. A conventional one-step reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) (cvPCR) method and a quantitative one-step RT-PCR (qPCR) method were developed to detect the SFTSV genome. Both cvPCR and qPCR detected a Chinese SFTSV strain. Forty-one of 108 Japanese patients suspected of having SFTS showed a positive reaction by cvPCR. The results from the samples of 108 Japanese patients determined by the qPCR method were in almost complete agreement with those determined by cvPCR. The analyses of the viral copy number level in the patient blood samples at the acute phase determined by qPCR in association with the patient outcome confirmed that the SFTSV RNA load in the blood of the nonsurviving patients was significantly higher than that of the surviving patients. Therefore, the cvPCR and qPCR methods developed in this study can provide a powerful means for diagnosing SFTS. In addition, the detection of the SFTSV genome level by qPCR in the blood of the patients at the acute phase may serve as an indicator to predict the outcome of SFTS.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, Zhang L, Zhang QF, Popov VL, Li C, Qu J, Li Q, Zhang YP, Hai R, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhan FX, Wang XJ, Kan B, Wang SW, Wan KL, Jing HQ, Lu JX, Yin WW, Zhou H, Guan XH, Liu JF, Bi ZQ, Liu GH, Ren J, Wang H, Zhao Z, Song JD, He JR, Wan T, Zhang JS, Fu XP, Sun LN, Dong XP, Feng ZJ, Yang WZ, Hong T, Zhang Y, Walker DH, Wang Y, Li DX. 2011. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 364:1523–1532. 10.1056/NEJMoa1010095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Xiong Y, Chen XP, He YW, Sun Q, Yu B, Li J, Dai YA, Tian JH, Qin XC, Jin D, Cui Z, Luo XL, Li W, Lu S, Wang W, Peng JS, Guo WP, Li MH, Li ZJ, Zhang S, Chen C, Wang Y, de Jong MD, Xu J. 2011. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel tick-borne bunyavirus in Huaiyangshan, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 32:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Xu B, Liu L, Huang X, Ma H, Zhang Y, Du Y, Wang P, Tang X, Wang H, Kang K, Zhang S, Zhao G, Wu W, Yang Y, Chen H, Mu F, Chen W. 2011. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 7:e1002369. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, Ishido A, Shigeoka T, Tominaga T, Kamei T, Honda M, Ninomiya D, Sakai T, Senba T, Kaneyuki S, Sakaguchi S, Satoh A, Hosokawa T, Kawabe Y, Kurihara S, Izumikawa K, Kohno S, Azuma T, Suemori K, Yasukawa M, Mizutani T, Omatsu T, Katayama Y, Miyahara M, Ijuin M, Doi K, Okuda M, Umeki K, Saito T, Fukushima K, Nakajima K, Yoshikawa T, Tani H, Fukushi S, Fukuma A, Ogata M, Shimojima M, Nakajima N, Nagata N, Katano H, Fukumoto H, Sato Y, Hasegawa H, Yamagishi T, Oishi K, Kurane I, Morikawa S, Saijo M. 2014. The first identification and retrospective study of severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 209:816-827. 10.1093/infdis/jit603. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

