Predictors of effectiveness of early intervention on children with intellectual disability: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 24989708
- PMCID: PMC4094398
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-170
Predictors of effectiveness of early intervention on children with intellectual disability: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The Taiwanese government has been promoting early intervention to children with intellectual disability for years, but data on its effectiveness are limited.
Methods: We recruited children who were treated for intellectual disability at a teaching hospital and had two IQ tests from 2001 to 2005 and used the difference between the two tests as the indicator of effectiveness.
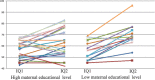
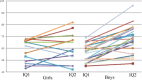
Results: The participants included 23 boys and 13 girls 56.5 ± 5.9 months of age at the first test and 73.4 ± 4.9 months at the second. The IQ increased from 57.0 ± 8.0 to 65.1 ± 12.3 (p < 0.001). Multi-variate regressions showed that a low maternal educational level, male gender, and a younger age at the first test were significant independent predictors of the effectiveness.
Conclusions: Early intervention can improve the IQ of children with intellectual disability, and the earlier the intervention the better. The effectiveness is demonstrable in boys and more prominent in children whose mothers had a low educational level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IQ at age 12 following a history of institutional care: Findings from the Bucharest Early Intervention Project.Dev Psychol. 2016 Nov;52(11):1858-1866. doi: 10.1037/dev0000167. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Dev Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27709994 Free PMC article.
-
Early intervention in developmental delay.Indian J Pediatr. 2008 Apr;75(4):393-7. doi: 10.1007/s12098-008-0044-3. Epub 2008 May 18. Indian J Pediatr. 2008. PMID: 18536896
-
The effectiveness of VIPP-V parenting training for parents of young children with a visual or visual-and-intellectual disability: study protocol of a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Sep 9;16:401. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0916-6. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26353825 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beginning reading interventions for children and adolescents with intellectual disability.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 5;12(12):CD011359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011359.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31805208 Free PMC article.
-
Early childhood predictors of global competence in adolescence for youth with typical development or intellectual disability.Res Dev Disabil. 2019 Nov;94:103462. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2019.103462. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Res Dev Disabil. 2019. PMID: 31499378 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of an App for Tracking Family Engagement With Early Intervention Services: Focus Groups and Pilot Evaluation Study.JMIR Hum Factors. 2023 Sep 12;10:e45957. doi: 10.2196/45957. JMIR Hum Factors. 2023. PMID: 37698912 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of young children with developmental delays and their trends over 14 years in Taiwan: a population-based nationwide study.BMJ Open. 2018 May 8;8(5):e020994. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020994. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29739783 Free PMC article.
-
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Presenting as Incidental Hyper-Transaminasasemia in a Two-Month-Old Male.Cureus. 2023 Feb 26;15(2):e35498. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35498. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37007358 Free PMC article.
-
Language and Culture Backgrounds of Mothers and Child Development: A Nationwide Study on the Incidence of Developmental Delays in Children Born to Immigrant Mothers in Taiwan.Front Public Health. 2021 Aug 24;9:646444. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.646444. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34504823 Free PMC article.
-
Language and Ageing in Adults With Down Syndrome: An Analysis of Receptive and Expressive Language Measures.J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025 Jan;38(1):e13330. doi: 10.1111/jar.13330. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025. PMID: 39647848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Yeargin-Allsopp M, Murphy CC, Oakley GP, Sikes RK. A multiple-source method for studying the prevalence of developmental disabilities in children: the metropolitan Atlanta developmental disabilities study. Pediatrics. 1992;89:624–630. - PubMed
-
- Levy SE, Hyman SL. Pediatric assessment of the child with developmental delay. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1993;40:465–477. - PubMed
-
- American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. Definition of Intellectual Disability. Available from: http://www.aaidd.org [Date accessed: July 5, 2014]
-
- Simeonsson RJ. Primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention in early intervention. J Early Intervent. 1991;15:124–134. doi: 10.1177/105381519101500202. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources