Thrombin-induced platelet activation via PAR4: pivotal role for exosite II
- PMID: 24990072
- PMCID: PMC6374991
- DOI: 10.1160/TH13-12-1013
Thrombin-induced platelet activation via PAR4: pivotal role for exosite II
Abstract
Thrombin-induced platelet activation via PAR1 and PAR4 is an important event in haemostasis. Although the underlying mechanisms responsible for ensuring efficient PAR1 activation by thrombin have been extensively studied, the potential involvement of recognitions sites outside the active site of the protease in thrombin-induced PAR4 activation is largely unknown. In this study, we developed a new assay to assess the importance of exosite I and II for PAR4 activation with α - and γ-thrombin. Surprisingly, we found that exosite II is critical for activation of PAR4. We also show that this dependency on exosite II likely represents a new mechanism, as it is unaffected by blockage of the previously known interaction between thrombin and glycoprotein Ibα.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
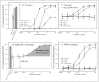
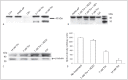
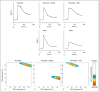


References
-
- Kahn ML, Zheng Y-W, Huang W. A dual thrombin receptor system for platelet activation. Nature. 1998;394:690–694. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro MJ, Weiss EJ, Faruqi TR. Protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 are shut off with distinct kinetics after activation by thrombin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25216–25221. - PubMed
-
- De Candia E, Hall SW, Rutella S. Binding of Thrombin to Glycoprotein Ib Accelerates the Hydrolysis of Par-1 on Intact Platelets. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:4692–4698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

