Detecting enzyme activities with exogenous MRI contrast agents
- PMID: 24990812
- PMCID: PMC4117811
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201402474
Detecting enzyme activities with exogenous MRI contrast agents
Abstract
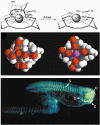
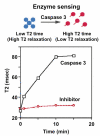
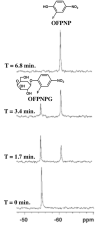
This review focuses on exogenous magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents that are responsive to enzyme activity. Enzymes can catalyze a change in water access, rotational tumbling time, the proximity of a (19)F-labeled ligand, the aggregation state, the proton chemical-exchange rate between the agent and water, or the chemical shift of (19)F, (31)P, (13)C or a labile (1)H of an agent, all of which can be used to detect enzyme activity. The variety of agents attests to the creativity in developing enzyme-responsive MRI contrast agents.
Keywords: CEST MRI; MR spectroscopy; enzymes; imaging agents; relaxation-based MRI.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


References
-
- Sittampalam GS. Assay Guidance Manual. Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; Bethesda MD: 2004. - PubMed
-
- Messerschmidt A, editor. Handbook of Metalloproteases. 2011.
- Adam JA. Chem. Rev. 2001,;101:2271–2290. - PubMed
- Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF, editors. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Academic Press; London: 1998.
-
- Gatti-Lafranconi P, Hollfelder F. ChemBioChem. 2013;14:285–292. - PubMed
-
- Moffitt JR, Chemla YR, Bustamante C. Methods in Enzymology (Single Molecule Tools, Part B) 2010:221–257. - PubMed
-
- Maeng HJ, Chow ECY, Fan J, Pang KS. In: Encyclopedia of Drug Metabolism and Interactions. Lyubimov AV, Rodrigues AD, Sinz MA, editors. 2012. pp. 637–684.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

