Countdown to 2015 and beyond: fulfilling the health agenda for women and children
- PMID: 24990815
- PMCID: PMC7613194
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60925-9
Countdown to 2015 and beyond: fulfilling the health agenda for women and children
Abstract
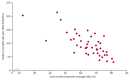
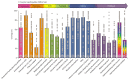
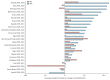
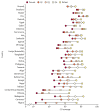
The end of 2015 will signal the end of the Millennium Development Goal era, when the world can take stock of what has been achieved. The Countdown to 2015 for Maternal, Newborn, and Child Survival (Countdown) has focused its 2014 report on how much has been achieved in intervention coverage in these groups, and on how best to sustain, focus, and intensify efforts to progress for this and future generations. Our 2014 results show unfinished business in achievement of high, sustained, and equitable coverage of essential interventions. Progress has accelerated in the past decade in most Countdown countries, suggesting that further gains are possible with intensified actions. Some of the greatest coverage gaps are in family planning, interventions addressing newborn mortality, and case management of childhood diseases. Although inequities are pervasive, country successes in reaching of the poorest populations provide lessons for other countries to follow. As we transition to the next set of global goals, we must remember the centrality of data to accountability, and the importance of support of country capacity to collect and use high-quality data on intervention coverage and inequities for decision making. To fulfill the health agenda for women and children both now and beyond 2015 requires continued monitoring of country and global progress; Countdown is committed to playing its part in this effort.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Victora CG, Fenn B, Bryce J, Kirkwood BR. Co-coverage of preventive interventions and implications for child-survival strategies: evidence from national surveys. Lancet. 2005;366:1460–66. - PubMed
-
- Filmer D, Pritchett LH. Estimating wealth effects without expenditure data-or tears: an application to educational enrollments in states of India. Demography. 2001;38:115–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

