The CNS glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor in the control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 24990862
- PMCID: PMC4166762
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00096.2014
The CNS glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor in the control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
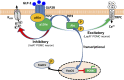
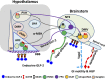
The gut-brain axis plays a key role in the control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. In response to luminal stimulation of macronutrients and microbiota-derived metabolites (secondary bile acids and short chain fatty acids), glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1 and -2) are cosecreted from endocrine L cells in the gut and coreleased from preproglucagonergic neurons in the brain stem. Glucagon-like peptides are proposed as key mediators for bariatric surgery-improved glycemic control and energy balance. Little is known about the GLP-2 receptor (Glp2r)-mediated physiological roles in the control of food intake and glucose homeostasis, yet Glp1r has been studied extensively. This review will highlight the physiological relevance of the central nervous system (CNS) Glp2r in the control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis and focuses on cellular mechanisms underlying the CNS Glp2r-mediated neural circuitry and intracellular PI3K signaling pathway. New evidence (obtained from Glp2r tissue-specific KO mice) indicates that the Glp2r in POMC neurons is essential for suppressing feeding behavior, gastrointestinal motility, and hepatic glucose production. Mice with Glp2r deletion selectively in POMC neurons exhibit hyperphagic behavior, accelerated gastric emptying, glucose intolerance, and hepatic insulin resistance. GLP-2 differentially modulates postsynaptic membrane excitability of hypothalamic POMC neurons in Glp2r- and PI3K-dependent manners. GLP-2 activates the PI3K-Akt-FoxO1 signaling pathway in POMC neurons by Glp2r-p85α interaction. Intracerebroventricular GLP-2 augments glucose tolerance, suppresses glucose production, and enhances insulin sensitivity, which require PI3K (p110α) activation in POMC neurons. Thus, the CNS Glp2r plays a physiological role in the control of food intake and glucose homeostasis. This review will also discuss key questions for future studies.
Keywords: central nervous system; food intake; gastric emptying; glucagon-like peptides; glucose homeostasis; gut-brain axis; insulin sensitivity.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Qassab H, Smith MA, Irvine EE, Guillermet-Guibert J, Claret M, Choudhury AI, Selman C, Piipari K, Clements M, Lingard S, Chandarana K, Bell JD, Barsh GS, Smith AJ, Batterham RL, Ashford ML, Vanhaesebroeck B, Withers DJ. Dominant role of the p110beta isoform of PI3K over p110alpha in energy homeostasis regulation by POMC and AgRP neurons. Cell Metab 10: 343–354, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amato A, Baldassano S, Serio R, Mule F. Glucagon-like peptide-2 relaxes mouse stomach through vasoactive intestinal peptide release. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296: G678–G684, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Amato A, Baldassano S, Serio R, Mule F. Glucagon-like peptide-2 relaxes mouse stomach through vasoactive intestinal peptide release. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296: G678–G684, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Amato A, Rotondo A, Cinci L, Baldassano S, Vannucchi MG, Mule F. Role of cholinergic neurons in the motor effects of glucagon-like peptide-2 in mouse colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299: G1038–G1044, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Anini Y, Brubaker PL. Role of leptin in the regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Diabetes 52: 252–259, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

