Quantification of allicin by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet analysis with effect of post-ultrasonic sound and microwave radiation on fresh garlic cloves
- PMID: 24991105
- PMCID: PMC4078350
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.133279
Quantification of allicin by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet analysis with effect of post-ultrasonic sound and microwave radiation on fresh garlic cloves
Abstract
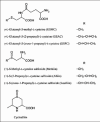
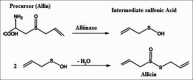
Background: Garlic (Allium sativum L.) has been accepted universally to be applied in food, spice and traditional medicine. The medicinal and other beneficial properties of garlic are attributed to organosulfur compounds.
Objective: As of today no simultaneous analysis has been performed; hence the transformation of allicin to its degraded products during cultivation and storage is open into doubt.
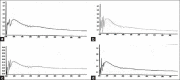
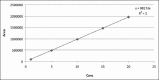
Materials and methods: In our present work, we have tried to develop a sensitive and reproducible analytical method to measure allicin by high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet analysis with effect of post-acoustic waves and microwave radiation on fresh garlic cloves.
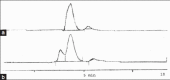
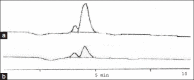
Results: The process revealed the effect of different radiation techniques on fresh garlic retains the principle component, allicin in its pure form and generated higher yield than the conventional way of extraction.
Conclusion: Therefore, materializing these techniques in the pharmaceutical industry will definitely be proved beneficial in term of time as well as money. Most interestingly, the methods ruled out possibilities of degradation of organosulfur compounds as well.
Keywords: Acoustic waves; allicin; garlic; high performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet analysis; microwave radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Young NJ, Yong-Hoon C, Chul-Hak Y. Identification of an essential tryptophan residue in alliinase from garlic (Allium sativum) by chemical modification. Bull Korean Chem Soc. 2001;22:68–76.
-
- Hans-Peter K. Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Chemie und Pharmazie der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München; 2003. Interaction of Allium sativum L. and Leontopodium alpinum cass. with mediators of inflammation involved in the molecular mechanisms of atherosclerosis.
-
- Mukherjee M, Das AS, Das D, Mukherjee S, Mitra S, Mitra C. Role of oil extract of garlic (Allium sativum Linn.). on intestinal transference of calcium and its possible correlation with preservation of skeletal health in an ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis. Phytother Res. 2006;20:408–15. - PubMed
-
- Raghuveer C. Benificial effect of Allium sativum and Allium tuberosum on experimental hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Pak J Physiol. 2008;4:7–9.
-
- Dkhil MA, Abdel-Baki AS, Wunderlich F, Sies H, Al-Quraishy S. Anticoccidial and antiinflammatory activity of garlic in murine Eimeria papillata infections. Vet Parasitol. 2011;175:66–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
