Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols, tannins and epigallocatechin gallate from barks of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.) Coville bark extracts
- PMID: 24991110
- PMCID: PMC4078346
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.133287
Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols, tannins and epigallocatechin gallate from barks of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.) Coville bark extracts
Abstract
Background: Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mar.) Coville is a native plant from Brazil, rich in phenolic compounds and used on popular medicine as a wound healing agent, in the treatment of gastric lesions and as antimicrobial.
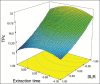
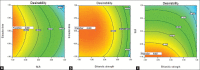
Materials and methods: Ultrassound-assisted extraction (UAE) was applied to extraction of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), total polyphenols (TP) and total tannins (TT) content from barks of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mar.) Coville. Several operating parameters, namely extraction time (min), liquid to solid ratio (mg/mL), ethanolic strength (%, v/v), were optimized using response surface methodology (RSM) with a Box-Behnken design.
Results: By using the desirability function approach, the optimum UAE conditions to obtain desirable extraction yields for all these metabolites simultaneously were found at the extraction time of 30 min, solid to liquid ratio of 4 mg/mL and ethanolic strength of 65. Under these conditions, the epigallocatechin gallate, total polyphenols and total tannins content were 0.31; 22.95 and 11.95 % (w/w), respectively.
Conclusion: The results indicated that knowledge gained from this study should be helpful to further exploit and apply this resource and also showed the feasibility of ultrasound-assisted extraction for obtaining GEGC, TP and TT from barks of S. adstrigens.
Keywords: Desirability function; Stryphnodendron adstringens; optimization; response surface methodology; ultrassound-assisted extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Myrcia amazonica DC. (Myrtaceae) Leaves.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 Jan-Mar;12(45):9-12. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.175997. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27019555 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of traditionality of Brazilian medicinal plants: The case studies of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.) Coville (barbatimão) barks and Copaifera spp. (copaíba) oleoresin in wound healing.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:319-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.042. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29501844
-
Microwave irradiation to the rapid extraction of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Barbatimão) compounds by statistical planning.Nat Prod Res. 2021 Jan;35(2):354-358. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1628748. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Nat Prod Res. 2021. PMID: 31184511
-
Proanthocyanidin polymeric tannins from Stryphnodendron adstringens are effective against Candida spp. isolates and for vaginal candidiasis treatment.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Apr 24;216:184-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29325916
-
Amphipterygium adstringens (Schltdl.) Schiede ex Standl (Anacardiaceae): An Endemic Plant with Relevant Pharmacological Properties.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jul 2;11(13):1766. doi: 10.3390/plants11131766. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35807718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and pharmacokinetics in beagle dogs of ganershu sustained-release pellets.Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):217-26. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.137360. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014. PMID: 25210307 Free PMC article.
-
Development of response surface methodology for optimization of extraction parameters and quantitative estimation of embelin from Embelia ribes Burm by high performance liquid chromatography.Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 May;11(Suppl 1):S166-72. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.157722. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015. PMID: 26109763 Free PMC article.
-
Feature-Based Molecular Network-Guided Dereplication of Natural Bioactive Products from Leaves of Stryphnodendron pulcherrimum (Willd.) Hochr.Metabolites. 2021 Apr 29;11(5):281. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050281. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33946668 Free PMC article.
-
Stryphnodendron Species Known as "Barbatimão": A Comprehensive Report.Molecules. 2018 Apr 15;23(4):910. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040910. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29662029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Incorporated with the Antioxidant Extract of Stryphnodendron adstringens Bark.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;14(22):4806. doi: 10.3390/polym14224806. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agra MF, Silva KN, Basílio IJ, Freitas PF, Barbosa-Filho JM. Survey of medicinal plants used in the region Northeast of Brazil. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2008;18:472–508.
-
- Audi EA, Toledo DP, Peres PG, Kimura E, Pereira WK, de Mello JC, et al. Gastric antiulcerogenic effects of Stryphnodendron adstringens in rats. Phytother Res. 1999;13:264–6. - PubMed
-
- Martins DT, Lima JC, Rao VS. The acetone soluble fraction from bark extract of Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.). Coville inhibits gastric acid secretion and experimental gastric ulceration in rats. Phytother Res. 2002;16:427–31. - PubMed
-
- Herzog-Soares JD, Alves RK. Trypanocidal activity in vivo of Stryphnodendron adstringens (true barbatimão) and Caryocar brasiliensis (pequi) Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2002;12:2–4.
-
- Audi EA. Biological Activity and Quality Control of Extract and Stem Bark From Stryphnodendron adstringens. Acta Farm Bonaer. 2004;23:328–33.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
