The effects of 3% diquafosol sodium application on the tear functions and ocular surface of the Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase-1 (Sod1)-knockout mice
- PMID: 24991185
- PMCID: PMC4077595
The effects of 3% diquafosol sodium application on the tear functions and ocular surface of the Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase-1 (Sod1)-knockout mice
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the role of a water and mucin secretagogue (3% diquafosol sodium eye drops) on the tear function and conjunctival ocular surface changes in Sod1(-/-) in comparison to the wild-type (WT) mice.
Methods: Fourteen eyes of 7 Sod1(-/-) male mice with C57BL/background and 14 eyes of 7 C57BL6 strain wild-type male mice were examined at 40 weeks in this study. All mice had application of 3% diquafosol ophthalmic solution six times a day for 2 weeks. Tear film stability and corneal epithelial damage was evaluated by fluorescein and Rose Bengal stainings. Anterior segment photography was performed before and after eye drop instillations. Aqueous tear quantity was measured with phenol red-impregnated cotton threads without anesthesia. Animals were sacrificed at 42 weeks after diquafosol treatment and the whole globe specimens were subjected to periodic acid Schiff staining. Goblet cell density was quantified by J Image software. Quantitative real-time PCR for conjunctival muc 5AC messenger RNA expression was also performed.
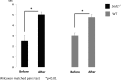
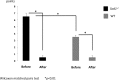
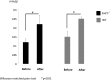
Results: Sod1(-/-) mice had significantly higher fluorescein staining scores compared to the WT mice before eye drop instillation. The mean tear film breakup time, Rose Bengal staining scores, and muc5 messenger RNA expression improved significantly with diquafosol treatment in both the WT and the knockout mice. The mean fluorescein staining score and aqueous tear quantity significantly improved in the Sod1(-/-) mice with treatment. A notable and consistent increase in goblet cells and decrease in inflammatory cell infiltrates could be confirmed in all specimens after 2 weeks of diquafosol eye drop application.
Conclusions: Three percent diquafosol ophthalmic solution appears to be effective in the treatment of ocular surface disease in this age-related dry eye disease mouse model.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The effects of 3% diquafosol sodium eye drop application on meibomian gland and ocular surface alterations in the Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase-1 (Sod1) knockout mice.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018 Apr;256(4):739-750. doi: 10.1007/s00417-018-3932-x. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29484560
-
The effects of 2% rebamipide ophthalmic solution on the tear functions and ocular surface of the superoxide dismutase-1 (sod1) knockout mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Nov 21;54(12):7793-802. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13128. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24168989
-
Comparison of Short-Term Effects of Diquafosol and Rebamipide on Mucin 5AC Level on the Rabbit Ocular Surface.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jul/Aug;33(6):493-497. doi: 10.1089/jop.2016.0092. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28346860
-
Diquafosol ophthalmic solution 3 %: a review of its use in dry eye.Drugs. 2015 May;75(8):911-22. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0409-7. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25968930 Review.
-
Diquafosol ophthalmic solution for dry eye treatment.Adv Ther. 2012 Jul;29(7):579-89. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0033-9. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Adv Ther. 2012. PMID: 22843206 Review.
Cited by
-
Topical diquafosol versus hyaluronic acid for the treatment of dry eye disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 Dec;261(12):3355-3367. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06083-4. Epub 2023 May 10. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37162564
-
A New Perspective on Dry Eye Classification: Proposal by the Asia Dry Eye Society.Eye Contact Lens. 2020 Jan;46 Suppl 1(1):S2-S13. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000643. Eye Contact Lens. 2020. PMID: 31425351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of Evaporative Dry Eye With Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Model Mice by Treatment With Ophthalmic Solution Containing Mineral Oil.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021 Apr 1;10(4):21. doi: 10.1167/tvst.10.4.21. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34003999 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory increases in tear volume and mucin levels associated with meibomian gland dysfunction caused by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 deficiency.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 20;8(1):3358. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21542-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29463801 Free PMC article.
-
A Prospective, Randomized Trial of Two Mucin Secretogogues for the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome in Office Workers.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 9;7(1):15210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13121-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29123104 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Uchino M, Dogru M, Yagi Y, Goto E, Tomita M, Kon T, Saiki M, Matsumoto Y, Uchino Y, Yokoi N, Kinoshita S, Tsubota K. The features of dry eye disease in a Japanese elderly population. Optom Vis Sci. 2006;83:797–802. - PubMed
-
- Spector A. Oxidative stress-induced cataract: mechanism of action. FASEB J. 1995;9:1173–82. - PubMed
-
- Gritz DC, Montes C, Atalla LR, Wu GS, Sevanian A, Rao NA. Histochemical localization of superoxide production in experimental autoimmune uveitis. Curr Eye Res. 1991;10:927–31. - PubMed
-
- Niesman MR, Johnson KA, Penn JS. Therapeutic effect of liposomal superoxide dismutase in an animal model of retinopathy of prematurity. Neurochem Res. 1997;22:597–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

