Cardiotoxicity of concomitant radiotherapy and trastuzumab for early breast cancer
- PMID: 24991199
- PMCID: PMC4078028
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2013-0040
Cardiotoxicity of concomitant radiotherapy and trastuzumab for early breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab therapy given in combination with one of several chemotherapy regimens is currently considered the standard of care for the treatment of early-stage, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) -positive breast cancer. The treatment with trastuzumab is due to a significant impact on the survival part of the standard adjuvant treatment of patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Patients treated with postoperative breast or chest wall irradiation receive trastuzumab concomitant with radiotherapy. In a small proportion of patients trastuzumab causes cardiotoxicity. Preclinical findings indicate a radiosensibilizing effect of trastuzumab in breast cancer cells, but it is not yet clear whether it radiosensibilizes cells of healthy tissues too.
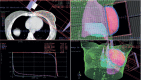
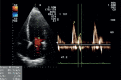
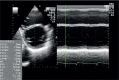
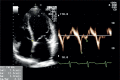
Conclusions: Special attention is required when left breast or left thoracic wall is irradiated in patient receiving trastuzumab, because long-term effects of the concurrent treatment with trastuzumab and radiotherapy are not yet known. In an era where more patients are surviving a diagnosis of breast cancer, better understanding and earlier detection of therapy-induced cardiac toxicity will be of paramount importance.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; early breast cancer; radiotherapy; trastuzumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential impact of cardiac dose-volume on acute cardiac toxicity following concurrent trastuzumab and radiotherapy.Cancer Radiother. 2014 Mar;18(2):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Cancer Radiother. 2014. PMID: 24642505
-
A phase 2 randomized trial to evaluate the impact of a supervised exercise program on cardiotoxicity at 3 months in patients with HER2 overexpressing breast cancer undergoing adjuvant treatment by trastuzumab: design of the CARDAPAC study.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jun 19;17(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3420-4. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28629338 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diastolic Dysfunction Occurs Early in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Treated Concurrently With Radiation Therapy and Trastuzumab.Oncologist. 2015 Jun;20(6):605-14. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0299. Epub 2015 May 1. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 25933931 Free PMC article.
-
One year versus a shorter duration of adjuvant trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan;173(2):247-254. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-5001-x. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30317424
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of clinical risk factors, pharmacologic prevention, and cardiotoxicity of other HER2-directed therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06280-x. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34115243 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer-Professional Guideline 1st Central-Eastern European Professional Consensus Statement on Breast Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2022 Jun 23;28:1610378. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610378. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 35832115 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Toxicity Under Concurrent Administration of Trastuzumab (Anti-HER2 Therapy) and Radiotherapy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 23;8(6):e70966. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70966. eCollection 2025 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40551859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect at One Year of Adjuvant Trastuzumab for HER2+ Breast Cancer Combined with Radiation or an Anthracycline on Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction.Am J Cardiol. 2020 Jun 15;125(12):1906-1912. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.03.013. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Am J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32331711 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Quality of Life Indicators and Cardiac Status Indicators in Chemotherapy Patients.Zdr Varst. 2021 Oct 20;60(4):199-209. doi: 10.2478/sjph-2021-0028. eCollection 2021 Dec. Zdr Varst. 2021. PMID: 34917188 Free PMC article.
-
Trastuzumab resumption after extremely severe cardiotoxicity in metastatic breast cancer patient: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2017 Nov 7;17(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3712-8. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29115937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–82. - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE, Jr, Davidson NE, et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1673–84. - PubMed
-
- Smith I, Procter M, Gelber RD, Guillaume S, Feyereislova A, Dowsett M, et al. 2-year follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;369:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Matos E. [Treatment of HER2 positive breast cancer patients]. [Slovenian] Zdrav Vestn. 2012;81:236–45.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
