Proteomic analysis of effects by x-rays and heavy ion in HeLa cells
- PMID: 24991204
- PMCID: PMC4078033
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2013-0087
Proteomic analysis of effects by x-rays and heavy ion in HeLa cells
Abstract
Background: Carbon ion therapy may be better against cancer than the effects of a photon beam. To investigate a biological advantage of carbon ion beam over X-rays, the radioresistant cell line HeLa cells were used. Radiation-induced changes in the biological processes were investigated post-irradiation at 1 h by a clinically relevant radiation dose (2 Gy X-ray and 2 Gy carbon beam). The differential expression proteins were collected for analysing biological effects.
Materials and methods: The radioresistant cell line Hela cells were used. In our study, the stable isotope labelling with amino acids (SILAC) method coupled with 2D-LC-LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometry was applied to identity and quantify the differentially expressed proteins after irradiation. The Western blotting experiment was used to validate the data.
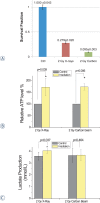
Results: A total of 123 and 155 significantly changed proteins were evaluated with treatment of 2 Gy carbon and X-rays after radiation 1 h, respectively. These deregulated proteins were found to be mainly involved in several kinds of metabolism processes through Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis. The two groups perform different response to different types of irradiation.
Conclusions: The radioresistance of the cancer cells treated with 2 Gy X-rays irradiation may be largely due to glycolysis enhancement, while the greater killing effect of 2 Gy carbon may be due to unchanged glycolysis and decreased amino acid metabolism.
Keywords: 2D-LC-MS/MS; Carbon ion; Gene Ontology enrichment; SILAC; X-rays.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Proteomic Analysis Implicates Dominant Alterations of RNA Metabolism and the Proteasome Pathway in the Cellular Response to Carbon-Ion Irradiation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0163896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163896. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711237 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of carbon ion beam on putative colon cancer stem cells and its comparison with X-rays.Cancer Res. 2011 May 15;71(10):3676-87. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2926. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21454414
-
WAF1 accumulation by carbon-ion beam and alpha-particle irradiation in human glioblastoma cultured cells.Int J Radiat Biol. 2000 Mar;76(3):335-41. doi: 10.1080/095530000138673. Int J Radiat Biol. 2000. PMID: 10757313
-
Differential Superiority of Heavy Charged-Particle Irradiation to X-Rays: Studies on Biological Effectiveness and Side Effect Mechanisms in Multicellular Tumor and Normal Tissue Models.Front Oncol. 2016 Feb 25;6:30. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00030. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26942125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Difference in Acquired Radioresistance Induction Between Repeated Photon and Particle Irradiation.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 12;9:1213. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01213. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31799186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Analysis Implicates Dominant Alterations of RNA Metabolism and the Proteasome Pathway in the Cellular Response to Carbon-Ion Irradiation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0163896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163896. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711237 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Glycolysis Confers Resistance Against Photon but Not Carbon Ion Irradiation in Human Glioma Cell Lines.Cancer Manag Res. 2023 Jan 4;15:1-16. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S385968. eCollection 2023. Cancer Manag Res. 2023. PMID: 36628255 Free PMC article.
-
Identify the signature genes for diagnose of uveal melanoma by weight gene co-expression network analysis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2015 Apr 18;8(2):269-74. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.02.10. eCollection 2015. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25938039 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of protein biomarkers and signaling pathways associated with prostate cancer radioresistance using label-free LC-MS/MS proteomic approach.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 22;7:41834. doi: 10.1038/srep41834. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28225015 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis in identification of metastasis-related genes of lung squamous cell carcinoma based on the Cancer Genome Atlas database.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Jan;9(1):42-53. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.01.04. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 28203405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi A, Ota I, Tamamoto T, Asakawa I, Nagata Y, Nakagawa H, et al. p53-dependent hyperthermic enhancement of tumour growth inhibition by X-ray or carbon-ion beam irradiation. Int J Hyperther. 2003;19:145–53. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto N, Ikeda C, Yakushiji T, Nomura T, Katakura A, Shibahara T, et al. Genetic effects of X-ray and carbon ion irradiation in head and neck carcinoma cell lines. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2007;48:177–85. - PubMed
-
- Cui X, Oonishi K, Tsujii H, Yasuda T, Matsumoto Y, Furusawa Y, et al. Effects of Carbon Ion Beam on Putative Colon Cancer Stem Cells and Its Comparison with X-rays. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3676–87. - PubMed
-
- Suit H, Urie M. Proton beams in radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer I. 1992;84:155–64. - PubMed
-
- Okayasu R, Okada M, Okabe A, Noguchi M, Takakura K, Takahashi S. Repair of DNA damage induced by accelerated heavy ions in mammalian cells proficient and deficient in the non-homologous end-joining pathway. Radiat Res. 2006;165:59–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
