Polymorphisms in folate pathway and pemetrexed treatment outcome in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 24991206
- PMCID: PMC4078035
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2013-0086
Polymorphisms in folate pathway and pemetrexed treatment outcome in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Introduction: A combination of pemetrexed and cisplatin has been shown to improve the outcome in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM), however, there is a great heterogeneity in treatment response among patients. The aim of our study was to evaluate the influence of polymorphisms in folate pathway and transporter genes on pemetrexed treatment outcome in Slovenian patients with MPM.
Methods: MPM patients treated with pemetrexed in the course of a prospective randomized clinical trial were genotyped for nineteen polymorphisms in five genes of folate pathway and six transporter genes. Logistic regression was used to assess the influence of polymorphisms on treatment efficacy and toxicity, while Cox regression was used to determine their influence on progression-free and overall survival.
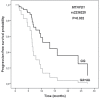
Results: Patients with at least one polymorphic MTHFD1 rs2236225 allele had a significantly lower response rate (p = 0.005; odds ratio [OR] = 0.12; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.03-0.54) and shorter progression-free survival (p = 0.032; hazard ratio [HR] = 3.10; 95% CI = 1.10-8.74) than non-carriers. Polymorphisms in transporter genes did not influence survival; however, several were associated with toxicity. Liver toxicity was significantly lower in carriers of polymorphic ABCC2 rs2273697 (p = 0.028; OR = 0.23; 95% CI = 0.06-0.85), SLCO1B1 rs4149056 (p = 0.028; OR = 0.23; 95% CI = 0.06-0.85) and rs11045879 (p = 0.014; OR = 0.18; 95% CI = 0.05-0.71) alleles compared to non-carriers, as well as in patients with SLCO1B1 GCAC haplotype (p = 0.048; OR = 0.17; 95% CI = 0.03-0.98). Gastrointestinal toxicity was much more common in patients with polymorphic ABCC2 rs717620 allele (p = 0.004; OR = 10.67; 95% CI = 2.15-52.85) and ABCC2 CAG haplotype (p = 0.006; OR = 5.67; 95% CI = 1.64-19.66).
Conclusions: MTHFD1 polymorphism affected treatment response and survival, while polymorphisms in ABCC2 and SLCO1B1 transporter genes influenced the risk for toxicity. These polymorphisms could serve as potential markers of pemetrexed treatment outcome in patients with MPM.
Keywords: folate pathway; mesothelioma; pemetrexed; polymorphism; toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Mineo TC, Ambrogi V. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: factors influencing the prognosis. Oncology (Williston Park) 2012;26:1164–75. - PubMed
-
- Lee CW, Murray N, Anderson H, Rao SC, Bishop W. Outcomes with first-line platinum-based combination chemotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: a review of practice in British Columbia. Lung Cancer. 2009;64:308–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous