Artefactual nanoparticle activation of the inflammasome platform: in vitro evidence with a nano-formed calcium phosphate
- PMID: 24991724
- PMCID: PMC4441531
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm.14.58
Artefactual nanoparticle activation of the inflammasome platform: in vitro evidence with a nano-formed calcium phosphate
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether in vitro experimental conditions dictate cellular activation of the inflammasome by apatitic calcium phosphate nanoparticles.
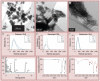
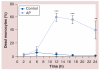
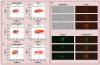
Material & methods: The responses of blood-derived primary human cells to in situ-formed apatite were investigated under different experimental conditions to assess the effect of aseptic culture, cell rest and duration of particle exposure. Cell death and particle uptake were assessed, while IL-1β and caspase 1 responses, with and without lipopolysaccharide prestimulation, were evaluated as markers of inflammasome activation.
Results: Under carefully addressed experimental conditions, apatitic nanoparticles did not induce cell death or engage the inflammasome platform, although both could be triggered through artefacts of experimentation.
Conclusion: In vitro studies often predict that engineered nanoparticles, such as synthetic apatite, are candidates for inflammasome activation and, hence, are toxic. However, the experimental setting must be very carefully considered as it may promote false-positive outcomes.
Keywords: IL-1β; apatite; caspase 1; experimental conditions; inflammasome; nanoparticle.
Figures


References
-
- Nel AE, Madler L, Velegol D, et al. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009;8(7):543–557. - PubMed
-
• Comprehensive review on the physicochemical factors that shape nanoparticle–cell interactions in biological surroundings.
-
- Powell JJ, Faria N, Thomas-McKay E, Pele LC. Origin and fate of dietary nanoparticles and microparticles in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Autoimmun. 2010;34(3):226–233. - PubMed
-
• Comprehensive review of the ‘bear traps’ in nanomineral characterization, definition and attribution of biological properties.
-
- Monopoli MP, Aberg C, Salvati A, Dawson KA. Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012;7(12):779–786. - PubMed
-
• Emphasizes the importance of the particle corona in dictating its biological outcome.
-
- Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006;440(7081):237–241. - PubMed
-
• Seminal work that set the scene in particle and inflammasome research.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
