Amelioration of cardiac function and activation of anti-inflammatory vasoactive peptides expression in the rat myocardium by low level laser therapy
- PMID: 24991808
- PMCID: PMC4081549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101270
Amelioration of cardiac function and activation of anti-inflammatory vasoactive peptides expression in the rat myocardium by low level laser therapy
Abstract
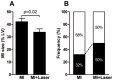
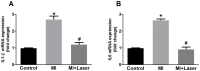
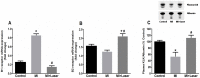
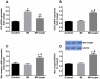
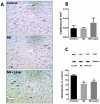
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) has been used as an anti-inflammatory treatment in several disease conditions, even when inflammation is a secondary consequence, such as in myocardial infarction (MI). However, the mechanism by which LLLT is able to protect the remaining myocardium remains unclear. The present study tested the hypothesis that LLLT reduces inflammation after acute MI in female rats and ameliorates cardiac function. The potential participation of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) and Kallikrein-Kinin System (KKS) vasoactive peptides was also evaluated. LLLT treatment effectively reduced MI size, attenuated the systolic dysfunction after MI, and decreased the myocardial mRNA expression of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 in comparison to the non-irradiated rat tissue. In addition, LLLT treatment increased protein and mRNA levels of the Mas receptor, the mRNA expression of kinin B2 receptors and the circulating levels of plasma kallikrein compared to non-treated post-MI rats. On the other hand, the kinin B1 receptor mRNA expression decreased after LLLT. No significant changes were found in the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the myocardial remote area between laser-irradiated and non-irradiated post-MI rats. Capillaries density also remained similar between these two experimental groups. The mRNA expression of the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was increased three days after MI, however, this effect was blunted by LLLT. Moreover, endothelial NOS mRNA content increased after LLLT. Plasma nitric oxide metabolites (NOx) concentration was increased three days after MI in non-treated rats and increased even further by LLLT treatment. Our data suggest that LLLT diminishes the acute inflammation in the myocardium, reduces infarct size and attenuates left ventricle dysfunction post-MI and increases vasoactive peptides expression and nitric oxide (NO) generation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
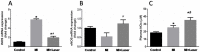
Similar articles
-
Myocardial angiogenesis induced by exercise training involves a regulatory mechanism mediated by kinin receptors.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2021 Jul 4;43(5):408-415. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2021.1896725. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 33687297
-
Nitric oxide mediates cardiac protection of tissue kallikrein by reducing inflammation and ventricular remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.Life Sci. 2008 Jan 16;82(3-4):156-65. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 9. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18068196 Free PMC article.
-
Novel anti-thrombotic mechanisms mediated by Mas receptor as result of balanced activities between the kallikrein/kinin and the renin-angiotensin systems.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Oct;160:105096. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105096. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32712319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kallikrein gene delivery improves cardiac reserve and attenuates remodeling after myocardial infarction.Hypertension. 2002 Nov;40(5):653-9. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.0000036035.41122.99. Hypertension. 2002. PMID: 12411458
-
Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors.Neuropeptides. 2010 Apr;44(2):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.004. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20045558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of low-level laser physiotherapy on left ventricular function among patients with chronic systolic heart failure.Egypt Heart J. 2023 Feb 13;75(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s43044-023-00337-6. Egypt Heart J. 2023. PMID: 36780088 Free PMC article.
-
Key inflammatory players for infarcted mass and cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 18;12:1609705. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1609705. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40756604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photobiomodulation Leads to Reduced Oxidative Stress in Rats Submitted to High-Intensity Resistive Exercise.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Feb 13;2018:5763256. doi: 10.1155/2018/5763256. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29636849 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation reduces oral mucositis by modulating NF-kB.J Biomed Opt. 2015;20(12):125008. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.12.125008. J Biomed Opt. 2015. PMID: 26720873
-
A Potential Role for Photobiomodulation Therapy in Disease Treatment and Prevention in the Era of COVID-19.Aging Dis. 2020 Dec 1;11(6):1352-1362. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0901. eCollection 2020 Dec. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 33269093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnston CI (1994) Tissue angiotensin converting enzyme in cardiac and vascular hypertrophy, repair, and remodeling. Hypertension 23: 258–268. - PubMed
-
- Bader M (2013) ACE2, angiotensin (1–7), and Mas: the other side of the coin. Pflugers Arch 465: 79–85. - PubMed
-
- Mello WD (2003) Effect of extracellular and intracellular angiotensins on heart cell function; on the cardiac renin-angiotensin system. Regul Pept 114: 87–90. - PubMed
-
- Marchesi C, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL (2008) Role of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29: 367–374. - PubMed
-
- Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM (2000) Reactive oxygen species and vascular cell apoptosis in response to angiotensin II and pro-atherosclerotic factors. Regul Pept 90: 19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

