Mitigation of experimental radiation nephropathy by renin-equivalent doses of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
- PMID: 24991882
- PMCID: PMC4402090
- DOI: 10.3109/09553002.2014.938375
Mitigation of experimental radiation nephropathy by renin-equivalent doses of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
Abstract
Purpose: We tested five different angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) as mitigators of experimental radiation nephropathy at drug doses calibrated to the plasma renin activity (PRA). This was done to determine whether all ACEI had the same efficacy as mitigators of radiation nephropathy when used at drug doses that gave equivalent suppression of the renin angiotensin system.
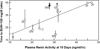
Method: 10 Gy total body irradiation with bone marrow transplantation was used to cause radiation nephropathy in barrier-maintained rats. Equivalent ACEI doses were determined based on their effect to inhibit angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) and raise the PRA in unirradiated animals.
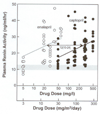
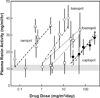
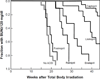
Results: PRA-equivalent doses were found for captopril, lisinopril, enalapril, ramipril and fosinopril. These doses overlap the human doses of these drugs on a body surface area basis. All ACE inhibitors, except fosinopril, mitigated radiation nephropathy; captopril was a somewhat better mitigator than lisinopril, enalapril or ramipril.
Conclusions: Most, but not all, ACEI mitigate radiation nephropathy at doses that overlap their clinically-used doses (on a body surface area basis). Fosinopril is known to be an ineffective mitigator of radiation pneumonitis, and it also does not mitigate radiation nephropathy. These pre-clinical data are critical in planning human studies of the mitigation of normal tissue radiation injury.
Keywords: ACE inhibitors; captopril; mitigation; plasma renin activity; radiation nephropathy; total body irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regression of ventricular and vascular hypertrophy: are there differences between structurally different angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors?J Hypertens. 2002 Dec;20(12):2495-504. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000042885.24999.e9. J Hypertens. 2002. PMID: 12473875
-
Model development and use of ACE inhibitors for preclinical mitigation of radiation-induced injury to multiple organs.Radiat Res. 2014 Nov;182(5):545-55. doi: 10.1667/RR13425.1. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 25361399 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo of the actions of seven structurally diverse inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE).Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;28 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):115S-130S; discussion 130S-131S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03587.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989. PMID: 2557876 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of radiation nephropathy with ACE inhibitors and AII type-1 and type-2 receptor antagonists.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(13):1317-25. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618821. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17506717 Review.
-
Mitigation of radiation injuries via suppression of the renin-angiotensin system: emphasis on radiation nephropathy.Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;11(11):1423-9. doi: 10.2174/1389450111009011423. Curr Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20583975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation-induced kidney toxicity: molecular and cellular pathogenesis.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;16(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01764-y. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33632272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Glucocorticoid Therapy on Guideline-Directed Medical Treatment Titration in Patients Hospitalized for Heart Failure with Low Blood Pressure: A Retrospective Study.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Oct 12;14:6693-6701. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S334132. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34675630 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear and Radiological Emergencies: Biological Effects, Countermeasures and Biodosimetry.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 31;11(6):1098. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061098. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35739995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saving normal tissues - a goal for the ages.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Jul;95(7):920-935. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1589654. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30822213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing Pharmaceuticals Previously Approved by Regulatory Agencies to Medically Counter Injuries Arising Either Early or Late Following Radiation Exposure.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 10;12:624844. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.624844. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34040517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Athyros VG, Mikhailidis DP, Kakafika AI, Tziomalos K, Karagiannis A. Angiotensin II reactivation and aldosterone escape phenomena in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade: is oral renin inhibition the solution? Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Berger R, Kuchling G, Frey B, Kozanly I, Pacher R, Stanek B. ACE inhibitor dosage at the time of listing predicts survival. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2000;19:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Brown NJ, Vaughan DE. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Circulation. 1998;97:1411–1420. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee KA. Simple linear regression. In: editors, editor. Statistical Theory and Methodology in Science and Engineering. 2nd edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1965. pp. 605–611.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
