Cell patterning for liver tissue engineering via dielectrophoretic mechanisms
- PMID: 24991941
- PMCID: PMC4168452
- DOI: 10.3390/s140711714
Cell patterning for liver tissue engineering via dielectrophoretic mechanisms
Abstract
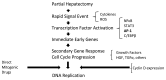
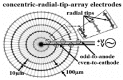
Liver transplantation is the most common treatment for patients with end-stage liver failure. However, liver transplantation is greatly limited by a shortage of donors. Liver tissue engineering may offer an alternative by providing an implantable engineered liver. Currently, diverse types of engineering approaches for in vitro liver cell culture are available, including scaffold-based methods, microfluidic platforms, and micropatterning techniques. Active cell patterning via dielectrophoretic (DEP) force showed some advantages over other methods, including high speed, ease of handling, high precision and being label-free. This article summarizes liver function and regenerative mechanisms for better understanding in developing engineered liver. We then review recent advances in liver tissue engineering techniques and focus on DEP-based cell patterning, including microelectrode design and patterning configuration.
Figures


References
-
- United Network for Organ Sharing. [(accessed on 29 November 2013)]. Available online: http://www.unos.org/#.
-
- Fishman J.A., Rubin R.H. Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;338:1741–1751. - PubMed
-
- Vacanti J.P., Langer R. Tissue engineering: The design and fabrication of living replacement devices for surgical reconstruction and transplantation. Lancet. 1999;354:SI32–34. - PubMed
-
- LeCluyse E.L., Bullock P.L., Parkinson A. Strategies for restoration and maintenance of normal hepatic structure and function in long-term cultures of rat hepatocytes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996;22:133–186.
-
- Goral V.N., Yuen P.K. Microfluidic platforms for hepatocyte cell culture: New technologies and applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012;40:1244–1254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

