Hippocampal memory traces are differentially modulated by experience, time, and adult neurogenesis
- PMID: 24991962
- PMCID: PMC4169172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.018
Hippocampal memory traces are differentially modulated by experience, time, and adult neurogenesis
Abstract
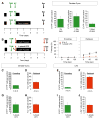
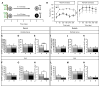
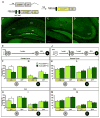
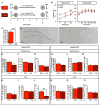
Memory traces are believed to be ensembles of cells used to store memories. To visualize memory traces, we created a transgenic line that allows for the comparison between cells activated during encoding and expression of a memory. Mice re-exposed to a fear-inducing context froze more and had a greater percentage of reactivated cells in the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA3 than mice exposed to a novel context. Over time, these differences disappeared, in keeping with the observation that memories become generalized. Optogenetically silencing DG or CA3 cells that were recruited during encoding of a fear-inducing context prevented expression of the corresponding memory. Mice with reduced neurogenesis displayed less contextual memory and less reactivation in CA3 but, surprisingly, normal reactivation in the DG. These studies suggest that distinct memory traces are located in the DG and in CA3 but that the strength of the memory is related to reactivation in CA3.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Regulation of hippocampal memory traces by neurogenesis.Neurogenesis (Austin). 2015 Sep 17;2(1):e1025180. doi: 10.1080/23262133.2015.1025180. eCollection 2015. Neurogenesis (Austin). 2015. PMID: 27604158 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Deletion or activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis and contextual fear memory.J Neurochem. 2013 May;125(3):430-45. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12130. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23240617 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal and ventral hippocampal adult-born neurons contribute to context fear memory.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Nov;43(12):2487-2496. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0109-6. Epub 2018 Jun 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29941977 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ablated hippocampal neurogenesis on the formation and extinction of contextual fear memory.Mol Brain. 2009 Jan 13;2:1. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-2-1. Mol Brain. 2009. PMID: 19138433 Free PMC article.
-
Inception of a false memory by optogenetic manipulation of a hippocampal memory engram.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 2;369(1633):20130142. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0142. Print 2014 Jan 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24298144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Aversive Memory by Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Neurotherapeutics. 2017 Jul;14(3):646-661. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0528-9. Neurotherapeutics. 2017. PMID: 28488160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contextual processing elicits sex differences in dorsal hippocampus activation following footshock and context fear retrieval.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Sep 1;393:112771. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112771. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32561387 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant ventral dentate gyrus structure and function in trauma susceptible mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 6;12(1):502. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02264-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36473832 Free PMC article.
-
Acute (R,S)-Ketamine Administration Induces Sex-Specific Behavioral Effects in Adolescent but Not Aged Mice.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 21;16:852010. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.852010. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35527817 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between α2-chimaerin and Rac1 activity determines dynamic maintenance of long-term memory.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 22;10(1):5313. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13236-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31757963 Free PMC article.
-
Age, sex, and apolipoprotein E isoform alter contextual fear learning, neuronal activation, and baseline DNA damage in the hippocampus.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Aug;28(8):3343-3354. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-01966-8. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36732588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartlett FC. Remembering: A Study in Experimental and Social Psychology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1932.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32 MH015174-36/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01MH099371-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007430/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH084529/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD017908/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH099371/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31MH084529-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH015174/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008798/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008798-8/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH068542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

