Functional genomics platform for pooled screening and generation of mammalian genetic interaction maps
- PMID: 24992097
- PMCID: PMC4144868
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2014.103
Functional genomics platform for pooled screening and generation of mammalian genetic interaction maps
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: functional genomics platform for pooled screening and generation of mammalian genetic interaction maps.Nat Protoc. 2015 Apr;10(4):643. doi: 10.1038/nprot0415-644d. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Nat Protoc. 2015. PMID: 25811902 No abstract available.
Abstract
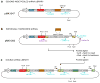
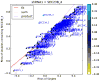
Systematic genetic interaction maps in microorganisms are powerful tools for identifying functional relationships between genes and for defining the function of uncharacterized genes. We have recently implemented this strategy in mammalian cells as a two-stage approach. First, genes of interest are robustly identified in a pooled genome-wide screen using complex shRNA libraries. Second, phenotypes for all pairwise combinations of 'hit' genes are measured in a double-shRNA screen and used to construct a genetic interaction map. Our protocol allows for rapid pooled screening under various conditions without a requirement for robotics, in contrast to arrayed approaches. Each round of screening can be implemented in ∼2 weeks, with additional time for analysis and generation of reagents. We discuss considerations for screen design, and we present complete experimental procedures, as well as a full computational analysis suite for the identification of hits in pooled screens and generation of genetic interaction maps. Although the protocol outlined here was developed for our original shRNA-based approach, it can be applied more generally, including to CRISPR-based approaches.
Figures






References
-
- Schuldiner M, et al. Exploration of the function and organization of the yeast early secretory pathway through an epistatic miniarray profile. Cell. 2005;123:507–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

