Genetic analysis of Leishmania donovani tropism using a naturally attenuated cutaneous strain
- PMID: 24992200
- PMCID: PMC4081786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004244
Genetic analysis of Leishmania donovani tropism using a naturally attenuated cutaneous strain
Abstract
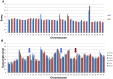
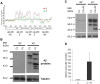
A central question in Leishmania research is why most species cause cutaneous infections but others cause fatal visceral disease. Interestingly, L. donovani causes both visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sri Lanka. L. donovani clinical isolates were therefore obtained from cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL-SL) and visceral leishmaniasis (VL-SL) patients from Sri Lanka. The CL-SL isolate was severely attenuated compared to the VL-SL isolate for survival in visceral organs in BALB/c mice. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis argue that gene deletions or pseudogenes specific to CL-SL are not responsible for the difference in disease tropism and that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and/or gene copy number variations play a major role in altered pathology. This is illustrated through the observations within showing that a decreased copy number of the A2 gene family and a mutation in the ras-like RagC GTPase enzyme in the mTOR pathway contribute to the attenuation of the CL-SL strain in visceral infection. Overall, this research provides a unique perspective on genetic differences associated with diverse pathologies caused by Leishmania infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Murray HW, Berman JD, Davies CR, Saravia NG (2005) Advances in leishmaniasis. Lancet 366: 1561–1577. - PubMed
-
- Karunaweera ND, Pratlong F, Siriwardane HVYD, Ihalamulla RL, Dedet JP (2003) Lankan cutaneous leishmaniasis is caused by Leishmania donovani zymodeme MON-37. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 97: 380–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

