Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 24992266
- PMCID: PMC4084629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099682
Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis
Abstract
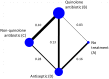
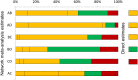
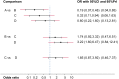
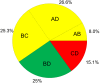
Systematic reviews that collate data about the relative effects of multiple interventions via network meta-analysis are highly informative for decision-making purposes. A network meta-analysis provides two types of findings for a specific outcome: the relative treatment effect for all pairwise comparisons, and a ranking of the treatments. It is important to consider the confidence with which these two types of results can enable clinicians, policy makers and patients to make informed decisions. We propose an approach to determining confidence in the output of a network meta-analysis. Our proposed approach is based on methodology developed by the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) Working Group for pairwise meta-analyses. The suggested framework for evaluating a network meta-analysis acknowledges (i) the key role of indirect comparisons (ii) the contributions of each piece of direct evidence to the network meta-analysis estimates of effect size; (iii) the importance of the transitivity assumption to the validity of network meta-analysis; and (iv) the possibility of disagreement between direct evidence and indirect evidence. We apply our proposed strategy to a systematic review comparing topical antibiotics without steroids for chronically discharging ears with underlying eardrum perforations. The proposed framework can be used to determine confidence in the results from a network meta-analysis. Judgements about evidence from a network meta-analysis can be different from those made about evidence from pairwise meta-analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Cipriani A, Higgins JPT, Geddes JR, Salanti G (2013) Conceptual and technical challenges in network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 159(2): 130–137. - PubMed
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, et al. (2011) GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence–indirectness. J Clin Epidemiol 64(12): 1303–1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

