Dual effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors on a rat model of inflammatory pain
- PMID: 24992453
- PMCID: PMC4273717
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/346105
Dual effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors on a rat model of inflammatory pain
Abstract
Background: Rho-kinases (ROCKs), a family of small GTP-dependent enzymes, are involved in a range of pain models, and their inhibition typically leads to antinociceptive effects.
Objectives: To study the effects of inhibiting ROCKs using two known inhibitors, Y27632 and HA1077 (fasudil), administered locally, on nociception and paw edema in rats.
Methods: A range of doses of Y27632 or HA1077 (2.5 μg to 1000 μg) were injected locally into rat paws alone or in combination with carrageenan, a known proinflammatory stimulus. Nociceptive responses to mechanical stimuli and increased paw volume, reflecting edema formation, were measured at 2 h and 3 h, using a Randall-Selitto apparatus and a hydroplethysmometer, respectively.
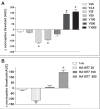
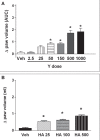
Results: Animals treated with either ROCK inhibitor showed biphasic nociceptive effects, with lower doses being associated with pronociceptive, and higher doses with antinociceptive responses. In contrast, a monophasic dose-dependent increase in edema was observed in the same animals. Local injection of 8-bromo-cyclic (c)GMP, an activator of the nitric oxide⁄cGMP⁄protein kinase G pathway, also produced biphasic effects on nociceptive responses in rat paws; however, low doses were antinociceptive and high doses were pronociceptive. Local administration of cytochalasin B, an inhibitor of actin polymerization and a downstream mediator of ROCK activity, reversed the antinociceptive effect of Y27632.
Conclusions: The results of the present study suggest that ROCKs participate in the local mechanisms associated with nociception⁄antinociception and inflammation, with a possible involvement of the nitric oxide⁄cGMP⁄protein kinase G pathway. Also, drug effects following local administration may differ markedly from the effects following systemic administration. Finally, separate treatment of pain and edema may be needed to maximize clinical benefit in inflammatory pain.
HISTORIQUE :: Les rho-kinases (ROCK), une famille de petits enzymes GTPases, participent à une série de modèles de douleur, et leur inhibition a généralement des effets antinociceptifs.
OBJECTIFS :: Étudier les effets de l’inhibition des ROCK au moyen de deux inhibiteurs connus administrés localement, le Y27632 et le HA1077 (fasudil), sur la nociception et l’œdème des pattes des rats.
MÉTHODOLOGIE :: Les chercheurs ont injecté une série de doses de Y27632 et de HA1077 (de 2,5 μg à 1 000 μg) dans les pattes de rats, seules ou en combinaison avec de la carraghénane, un stimulant proinflammatoire connu. Ils ont mesuré les réponses nociceptives aux stimuli mécaniques et à l’augmentation du volume des pattes, reflétant la formation d’œdème au bout de deux et trois heures, au moyen d’un test de Randall-Selitto et d’un hydro-pléthysmomètre, respectivement.
RÉSULTATS :: Les animaux traités avec l’un des inhibiteurs de la ROCK ont présenté des effets nociceptifs biphasiques, les doses moins élevées s’associant à une réponse pronociceptive et les doses plus élevées, à une réponse antinociceptive. Par contre, chez les mêmes animaux, on a observé une augmentation monophasique de l’œdème associée à la dose. L’injection locale de cGMP 8-bromo-cyclique, un activateur du monoxyde d’azote, du cGMP et de la voie de protéine kinase G, produisait également des effets biphasiques sur les réponses nociceptives des pattes de rats. Cependant, de faibles doses étaient antinociceptives et de fortes doses, pronociceptives. L’administration locale de cytochalasine B, un inhibiteur de la polymérisation de l’actine et un médiateur en aval de l’activité des ROCK, renversait l’effet antinociceptif du Y27632.
CONCLUSIONS :: D’après les résultats de la présente étude, les ROCK participent aux mécanismes locaux associés à la nociception ou à l’antinociception et à l’inflammation, peut-être en association avec le monozyde d’azote, le cGMP et la voie de la protéine kinase G. De plus, les effets des médicaments après leur administration locale peuvent différer considérablement de ceux consécutifs à leur administration systémique. Enfin, un traitement distinct de la douleur et de l’œdème peut s’imposer pour en maximiser les avantages cliniques en cas de douleur inflammatoire.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antinociceptive effects of AS1892802, a novel Rho kinase inhibitor, in rat models of inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Sep 1;334(3):955-63. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.167924. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20534789
-
Regulation of V-ATPase recycling via a RhoA- and ROCKII-dependent pathway in epididymal clear cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):C31-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00198.2010. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21411727 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Fasudil in preclinical models of pain.J Pain. 2010 Oct;11(10):941-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.12.014. Epub 2010 Mar 24. J Pain. 2010. PMID: 20338818
-
[Rho-kinase inhibitors].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2011 Sep;138(3):112-6. doi: 10.1254/fpj.138.112. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21908938 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology: the effect of fasudil.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;62(4):341-54. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182a3718f. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23921309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-selective inflammation in the oral cavity of the rat.Inflammopharmacology. 2016 Aug;24(4):145-53. doi: 10.1007/s10787-016-0269-0. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Inflammopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27324249
-
Daily low dose of tadalafil improves pain and frequency in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis patients.Turk J Urol. 2022 Jan;48(1):82-87. doi: 10.5152/tud.2022.21292. Turk J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35118993 Free PMC article.
-
Rho/ROCK acts downstream of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 in modulating P2X3 receptor-mediated bone cancer pain in rats.Mol Pain. 2016 Apr 18;12:1744806916644929. doi: 10.1177/1744806916644929. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27094551 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases in the Physiology and Pathophysiology of Peripheral Sensory Neurons.Cells. 2019 Jun 15;8(6):591. doi: 10.3390/cells8060591. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31208035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Riento K, Ridley AJ. ROCKs: Multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nature. 2003;4:446–54. - PubMed
-
- Hilgers RHP, Webb RC. Molecular aspects of arterial smooth muscle contraction: Focus on Rho. Exp Biol Med. 2005;230:829–35. - PubMed
-
- Nobes C, Hall A. Regulation and function of the Rho family of small GTPases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Fukata Y, Amano M, Kaibuchi K. Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharm Sci. 2001;22:32–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

