Computational prediction of microRNA networks incorporating environmental toxicity and disease etiology
- PMID: 24992957
- PMCID: PMC4081875
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05576
Computational prediction of microRNA networks incorporating environmental toxicity and disease etiology
Abstract
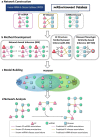
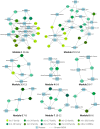
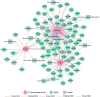
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in multiple biological processes and have attracted much scientific attention recently. Their expression can be altered by environmental factors (EFs), which are associated with many diseases. Identification of the phenotype-genotype relationships among miRNAs, EFs, and diseases at the network level will help us to better understand toxicology mechanisms and disease etiologies. In this study, we developed a computational systems toxicology framework to predict new associations among EFs, miRNAs and diseases by integrating EF structure similarity and disease phenotypic similarity. Specifically, three comprehensive bipartite networks: EF-miRNA, EF-disease and miRNA-disease associations, were constructed to build predictive models. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves using 10-fold cross validation ranged from 0.686 to 0.910. Furthermore, we successfully inferred novel EF-miRNA-disease networks in two case studies for breast cancer and cigarette smoke. Collectively, our methods provide a reliable and useful tool for the study of chemical risk assessment and disease etiology involving miRNAs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miREFRWR: a novel disease-related microRNA-environmental factor interactions prediction method.Mol Biosyst. 2016 Feb;12(2):624-33. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00697j. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 26689259
-
A novel framework for inferring condition-specific TF and miRNA co-regulation of protein-protein interactions.Gene. 2016 Feb 10;577(1):55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.11.023. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26611531
-
NEMPD: a network embedding-based method for predicting miRNA-disease associations by preserving behavior and attribute information.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 10;21(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03716-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32912137 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and their role in environmental chemical carcinogenesis.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Feb;41(1):225-247. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0179-8. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 30171477 Review.
-
A Computational Model to Predict the Causal miRNAs for Diseases.Front Genet. 2019 Oct 3;10:935. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00935. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31632446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network-based identification of microRNAs as potential pharmacogenomic biomarkers for anticancer drugs.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45584-45596. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10052. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27329603 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA networks in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Jan;18(1):5-18. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.99. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29170536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A network-based approach to uncover microRNA-mediated disease comorbidities and potential pathobiological implications.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2019 Nov 13;5:41. doi: 10.1038/s41540-019-0115-2. eCollection 2019. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31754458 Free PMC article.
-
A novel information diffusion method based on network consistency for identifying disease related microRNAs.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 30;8(64):36675-36690. doi: 10.1039/c8ra07519k. eCollection 2018 Oct 26. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35558942 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring potential small molecule-miRNA association based on triple layer heterogeneous network.J Cheminform. 2018 Jun 26;10(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13321-018-0284-9. J Cheminform. 2018. PMID: 29943160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee R. C., Feinbaum R. L. & Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Lee R. C. & Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294, 862–864 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–355 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

