Advances in astrocyte-targeted approaches for stroke therapy: an emerging role for mitochondria and microRNAS
- PMID: 24993363
- PMCID: PMC4284142
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-014-1373-4
Advances in astrocyte-targeted approaches for stroke therapy: an emerging role for mitochondria and microRNAS
Abstract
Astrocytes are critical regulators of neuronal function and an effective target for stroke therapy in animal models. Identifying individual targets with the potential for simultaneous activation of multiple downstream pathways that regulate astrocyte homeostasis may be a necessary element for successful clinical translation. Mitochondria and microRNAs each represent individual targets with multi-modal therapeutic potential. Mitochondria regulate metabolism and apoptosis, while microRNAs have the capacity to bind and inhibit numerous mRNAs. By combining strategies targeted at maintaining astrocyte function during and following cerebral ischemia, a synergistic therapeutic effect may be achieved.
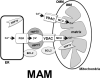
Figures


References
-
- Roger V, Go A, Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Berry J, Brown T, Carnethon M, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford E, Fox C, Fullerton H, Gillespie C, Greenlund K, Hailpern S, Heit J, Ho P, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lichtman J, Lisabeth L, Makuc D, Marcus G, Marelli A, Matchar D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Paynter N, Rosamond W, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Turan T, Turner M, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2011 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:e18–e209. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blakeley J, Llinas R. Thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2007;261:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Ogata K, Kosaka T. Structural and quantitative analysis of astrocytes in the mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2002;113:221–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

