Markers of eosinophilic inflammation for diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis and proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: a prospective study
- PMID: 24993367
- PMCID: PMC4252508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.06.019
Markers of eosinophilic inflammation for diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis and proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: a prospective study
Abstract
Background & aims: Distinguishing between eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), gastroesophageal reflux disease, and proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) is challenging. We assessed whether immunohistochemical analysis of esophageal tissues for major basic protein (MBP), eotaxin-3, and tryptase can be used for diagnosis of EoE and to differentiate EoE from PPI-REE.
Methods: We conducted a prospective study of 196 consecutive adults who underwent outpatient endoscopy at the University of North Carolina from 2009 through 2012. Incident cases of EoE were diagnosed per consensus guidelines. Patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease or dysphagia served as controls. PPI-REE was defined as a symptomatic and histologic response to a PPI. Immunohistochemistry was performed to quantify MBP, eotaxin-3, and tryptase. The maximum density of epithelial staining was determined for each assay; levels were compared between EoE and control groups and then EoE and PPI-REE groups, and receiver operating characteristic curves were constructed.
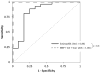
Results: Esophageal tissues from patients with EoE (n = 50) had a median 951 MBP-positive cells/mm(2), whereas those from controls (n = 123) had a median 2 MBP-positive cells/mm(2) (P < .001). Samples from patients with EoE had a median 155 eotaxin-3-positive cells/mm(2), and those from controls (n = 123) had 18 eotaxin-3-positive cells/mm(2) (P < .001). Samples from patients with EoE had a median 249 tryptase-positive cells/mm(2), and those from controls (n = 123) had 11 tryptase-positive cells/mm(2) (P < .001). Levels of MBP, eotaxin-3, tryptase, and the combination of all 3 identified patients with EoE with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.99, 0.94, 0.99, and 1.00. Analyses of only samples with eosinophil counts of 10-100 eosinophils per high-power field produced similar results. No marker distinguished EoE from PPI-REE. Esophageal tissues from patients with PPI-REE (n = 23) had 987 MBP-positive cells/mm(2) (P = .18, compared with EoE), 160 eotaxin-3-positive cells/mm(2) (P = .33), and 243 tryptase-positive cells/mm(2) (P = .28).
Conclusions: Esophageal tissues from patients with EoE have substantially higher levels of MBP, eotaxin-3, and tryptase than controls on the basis of immunohistochemical analysis. Assays for the 3 markers identify patients with EoE with 100% accuracy but cannot distinguish EoE from PPI-REE.
Keywords: AUCROC; Diagnostic; GERD; Immunohistochemical Assay; Validation.
Copyright © 2014 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None of the authors have competing interests related to this manuscript.
Figures

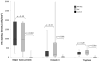
Comment in
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis and proton pump-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: what is in a name?Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Dec;12(12):2023-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.07.035. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25086198 No abstract available.
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of eosinophilic esophagitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Jun;13(6):1209-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.12.024. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25562797 No abstract available.
-
Reply: To PMID 24993367.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Jun;13(6):1210. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.02.039. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25737440 No abstract available.
References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, Burks AW, Chehade M, Collins MH, Dellon ES, Dohil R, Falk GW, Gonsalves N, Gupta SK, Katzka DA, Lucendo AJ, Markowitz JE, Noel RJ, Odze RD, Putnam PE, Richter JE, Romero Y, Ruchelli E, Sampson HA, Schoepfer A, Shaheen NJ, Sicherer SH, Spechler S, Spergel JM, Straumann A, Wershil BK, Rothenberg ME, Aceves SS. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20. e6. - PubMed
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras C, Katzka DA. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidence based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–92. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigo S, Abboud G, Oh D, Demeester SR, Hagen J, Lipham J, Demeester TR, Chandrasoma P. High intraepithelial eosinophil counts in esophageal squamous epithelium are not specific for eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:435–42. - PubMed
-
- Dranove JE, Horn DS, Davis MA, Kernek KM, Gupta SK. Predictors of response to proton pump inhibitor therapy among children with significant esophageal eosinophilia. J Pediatr. 2009;154:96–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

