A solid pseudopapillary neoplasm without cysts that occurred in a patient diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a case report
- PMID: 24993459
- PMCID: PMC4090630
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-243
A solid pseudopapillary neoplasm without cysts that occurred in a patient diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas is a rare neoplasm that has been reported to account for between 0.17% and 2.7% of all non-endocrine tumors of the pancreas. It is usually seen in young women. Because solid pseudopapillary neoplasms are rarely aggressive and have low-grade malignant potential and an excellent prognosis after complete resection, it is an ideal pancreatic tumor for treatment by minimally invasive surgery. Therefore, making an accurate pre-operative diagnosis is very important.
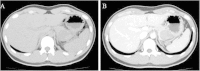
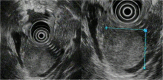
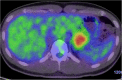
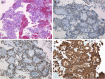
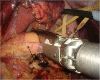
Case presentation: A 24-year-old Japanese man who had been found to have mild transaminase elevations at a medical check-up visited our hospital for further examination. Abdominal computed tomography showed a 40mm-diameter tumor in the pancreatic tail and mild fatty liver. He was admitted to our hospital for additional examination. The abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan taken at our institution showed an increasingly enhanced mass of 40mm diameter in the pancreatic tail. Ultrasonography showed a low-level echoic mass of 35mm diameter in the pancreatic tail. T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed low signal intensity in the tail of the pancreas. T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed high signal intensity there. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging showed high signal intensity. An endoscopic ultrasound yielded the same results as the abdominal ultrasonogram. In addition, [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography showed abnormal accumulation (maximum standardized uptake value, 6.53). This finding raised our suspicion of a pancreatic malignant tumor. However, the patient could not be confidently diagnosed solely on the basis of imaging. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration was performed, which led us to a diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. On that basis, we performed minimally invasive surgery (spleen-preserving laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy).
Conclusion: Atypical solid pseudopapillary neoplasm without cysts should be considered when diagnosing pancreatic tumors. A definitive pre-operative diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm made on the basis of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration can guide the surgical approach used.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

