The complex role of neuroinflammation in glaucoma
- PMID: 24993677
- PMCID: PMC4109578
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017269
The complex role of neuroinflammation in glaucoma
Abstract
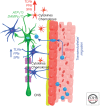
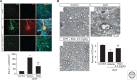
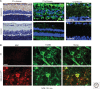
Glaucoma is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder affecting 80 million people worldwide. Loss of retinal ganglion cells and degeneration of their axons in the optic nerve are the major pathological hallmarks. Neuroinflammatory processes, inflammatory processes in the central nervous system, have been identified in human glaucoma and in experimental models of the disease. Furthermore, neuroinflammatory responses occur at early stages of experimental glaucoma, and inhibition of certain proinflammatory pathways appears neuroprotective. Here, we summarize the current understanding of neuroinflammation in the central nervous system, with emphasis on events at the optic nerve head during early stages of glaucoma.
Copyright © 2014 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed F, Brown KM, Stephan DA, Morrison JC, Johnson EC, Tomarev SI 2004. Microarray analysis of changes in mRNA levels in the rat retina after experimental elevation of intraocular pressure. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45: 1247–1258 - PubMed
-
- Bonifati DM, Kishore U 2007. Role of complement in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Mol Immunol 44: 999–1010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
