Association of Fascin and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression with poor prognostic parameters in breast carcinoma of Egyptian women
- PMID: 24993803
- PMCID: PMC4099107
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-136
Association of Fascin and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression with poor prognostic parameters in breast carcinoma of Egyptian women
Abstract
Background: The effects of fascin on cell invasiveness involve changes in cell motility and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity. Previous studies on the prognostic value of fascin and MMP-9 in breast carcinoma revealed conflicting results. To date, no immunohistochemical studies have been performed to assess the possible association between them in breast carcinoma. This study is designed to correlate their expression with prognostic parameters in breast carcinoma and assess the relationship between them.
Methods: Immunohistochemical expression of fascin and MMP-9 was evaluated semi quantitatively in 67 cases of breast carcinoma regarding the percentage of positive cells. Chi square test and Fisher's exact test were used to examine the relationship between categorical variables. Kappa statistics was used to compute the measure of agreement between two investigational methods.
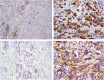
Results: Fascin and MMP-9 expressions were detected in 43.28% and 50.75% of breast carcinomas (respectively). Regarding the normal breast tissue, fascin expression was observed in myoepithelial cells and luminal cells of few ducts and acini. However, normal tissue showed negative MMP-9 expression. A significant relationship was observed between fascin and MMP-9 expression and lymph node metastases (p = 0.001 and 0.002 respectively), advanced tumor stage (p = 0.004 and 0.005 respectively), estrogen receptor negative (p = 0.002 and 0.005 respectively), progesterone receptor negative (p = 0.001 and 0.003 respectively) hormonal status and molecular subtypes (p = 0.0007 and 0.014 respectively). A significant strong agreement was detected between fascin and MMP-9 expression (p = 0.0001). More intense immunostaining of fascin and MMP-9 was observed at the invasive fronts compared with other areas of the tumor. Moreover, a significant moderate agreement between fascin and MMP-9 was found regarding the site of predominant intensity.
Conclusion: Fascin and MMP-9 proteins are associated with parameters of poor prognosis in breast cancer. The significant strong agreement between the two markers supports the role of fascin in cell invasiveness by activating matrix proteases besides increasing cell motility. Both proteins may represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with breast cancer especially those with hormone receptor-negative status.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/1421167695121127.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Strong association of fascin expression with triple negative breast cancer and basal-like phenotype in African-American women.J Clin Pathol. 2014 Feb;67(2):153-60. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201698. Epub 2013 Aug 28. J Clin Pathol. 2014. PMID: 23986556 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) correlates with poor prognoses of invasive breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2008 Mar 28;8:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-83. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18373849 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological significance of fascin and CD44v6 expression in endometrioid carcinoma.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Jul 11;7:80. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-80. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22784357 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of fascin, an actin-bundling motility protein, correlates with hormone receptor-negative breast cancer and a more aggressive clinical course.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 1;11(1):186-92. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15671545
-
The crucial role of fascin-1 in the pathogenesis, metastasis, and chemotherapeutic resistance of breast cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Feb;254:155079. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.155079. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38219494 Review.
Cited by
-
Fascin actin-bundling protein 1 in human cancer: promising biomarker or therapeutic target?Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Jan 20;20:240-264. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.12.014. eCollection 2021 Mar 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 33614909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Cancer Genetics and Genomics Studies in Africa.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 15;10:606400. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.606400. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33659210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fascin-1: Updated biological functions and therapeutic implications in cancer biology.BBA Adv. 2022 May 17;2:100052. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2022.100052. eCollection 2022. BBA Adv. 2022. PMID: 37082587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of matrix metalloproteinases 3 and 9 single nucleotide polymorphisms with breast cancer risk: A case-control study.Mol Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul;13(1):54-62. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2041. Epub 2020 May 5. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32454974 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Invasion and Metastasis by mPRα Through the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Pathol Oncol Res. 2016 Jul;22(3):471-6. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-0023-8. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016. PMID: 26608797
References
-
- Chambers AF, Naumov GN, Varghese HJ, Nadkarni KV, MacDonald IC, Groom AC. Critical steps in hematogenous metastasis: an overview. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2001;10:243–255. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto Y, Ito T, Inoue H, Okumura T, Tanaka E, Tsunoda S, Higashiyama M, Watanabe G, Imamura M, Shimada Y. Prognostic significance of fascin overexpression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(7):2597–2605. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto Y, Skacel M, Adams JC. Roles of fascin in human carcinoma motility and signaling: prospects for a novel biomarker? Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:1787–1804. - PubMed
-
- Kureishy N, Sapountzi V, Prag S, Anilkumar N, Adams JC. Fascins and their roles in cell structure and function. Bioessays. 2002;24:350–361. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

