NMR-based structural analysis of the complete rough-type lipopolysaccharide isolated from Capnocytophaga canimorsus
- PMID: 24993825
- PMCID: PMC4156048
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.571489
NMR-based structural analysis of the complete rough-type lipopolysaccharide isolated from Capnocytophaga canimorsus
Erratum in
-
NMR-based structural analysis of the complete rough-type lipopolysaccharide isolated from Capnocytophaga canimorsus.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 16;290(42):25273. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A114.571489. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26475523 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
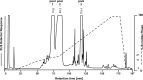
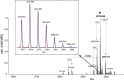
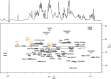
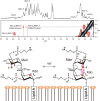
We here describe the NMR analysis of an intact lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin) in water with 1,2-dihexanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine as detergent. When HPLC-purified rough-type LPS of Capnocytophaga canimorsus was prepared, (13)C,(15)N labeling could be avoided. The intact LPS was analyzed by homonuclear ((1)H) and heteronuclear ((1)H,(13)C, and (1)H,(31)P) correlated one- and two-dimensional NMR techniques as well as by mass spectrometry. It consists of a penta-acylated lipid A with an α-linked phosphoethanolamine attached to C-1 of GlcN (I) in the hybrid backbone, lacking the 4'-phosphate. The hydrophilic core oligosaccharide was found to be a complex hexasaccharide with two mannose (Man) and one each of 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid (Kdo), Gal, GalN, and l-rhamnose residues. Position 4 of Kdo is substituted by phosphoethanolamine, also present in position 6 of the branched Man(I) residue. This rough-type LPS is exceptional in that all three negative phosphate residues are "masked" by positively charged ethanolamine substituents, leading to an overall zero net charge, which has so far not been observed for any other LPS. In biological assays, the corresponding isolated lipid A was found to be endotoxically almost inactive. By contrast, the intact rough-type LPS described here expressed a 20,000-fold increased endotoxicity, indicating that the core oligosaccharide significantly contributes to the endotoxic potency of the whole rough-type C. canimorsus LPS molecule. Based on these findings, the strict view that lipid A alone represents the toxic center of LPS needs to be reassessed.
Keywords: Capnocytophaga canimorsus; DHPC Micelles; Glycolipid Structure; Gram-negative Bacteria; High-performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC); Lipopolysaccharide (LPS); Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR).
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
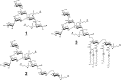



Similar articles
-
The lipopolysaccharide from Capnocytophaga canimorsus reveals an unexpected role of the core-oligosaccharide in MD-2 binding.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(5):e1002667. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002667. Epub 2012 May 3. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22570611 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the structure of an alanine-lacking core tetrasaccharide trisphosphate from the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant H4.Eur J Biochem. 1999 Apr;261(2):500-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00299.x. Eur J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10215862
-
Identification of a novel heptoglycan of alpha1-->2-linked D-glycero-D-manno-heptopyranose. Chemical and antigenic structure of lipopolysaccharides from Klebsiella pneumoniae ssp. pneumoniae rough strain R20 (O1-:K20-).J Biol Chem. 1998 Mar 20;273(12):7006-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.12.7006. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9507008
-
Structural analysis of the carbohydrate backbone of Vibrio parahaemolyticus O2 lipopolysaccharides.Carbohydr Res. 2003 May 1;338(10):1063-71. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(03)00078-8. Carbohydr Res. 2003. PMID: 12706972
-
Chemical and immunochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides of Coxiella burnetii phase I and phase II.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;228:577-91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1663-3_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988. PMID: 3051921 Review.
Cited by
-
The redefinition of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide O-antigen and core-oligosaccharide domains.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Mar 17;13(3):e1006280. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006280. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28306723 Free PMC article.
-
PplD is a de-N-acetylase of the cell wall linkage unit of streptococcal rhamnopolysaccharides.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 1;13(1):590. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28257-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35105886 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating endotoxin-biomolecule interactions with FRET: extending the frontiers of their supramolecular complexation.J Biol Methods. 2017 Apr 28;4(2):e71. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2017.172. eCollection 2017. J Biol Methods. 2017. PMID: 31453229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel structural features of the immunocompetent ceramide phospho-inositol glycan core from Trichomonas vaginalis.Carbohydr Res. 2016 Jan;419:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Carbohydr Res. 2016. PMID: 26671321 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a LOS and a capsular polysaccharide in Capnocytophaga canimorsus.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 15;6:38914. doi: 10.1038/srep38914. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27974829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oehler R. L., Velez A. P., Mizrachi M., Lamarche J., Gompf S. (2009) Bite-related and septic syndromes caused by cats and dogs. Lancet Infect. Dis. 9, 439–447 - PubMed
-
- Shin H., Mally M., Kuhn M., Paroz C., Cornelis G. R. (2007) Escape from immune surveillance by Capnocytophaga canimorsus. J. Infect. Dis. 195, 375–386 - PubMed
-
- Mally M., Paroz C., Shin H., Meyer S., Soussoula L. V., Schmiediger U., Saillen-Paroz C., Cornelis G. R. (2009) Prevalence of Capnocytophaga canimorsus in dogs and occurrence of potential virulence factors. Microbes Infect. 11, 509–514 - PubMed
-
- Pers C., Gahrn-Hansen B., Frederiksen W. (1996) Capnocytophaga canimorsus septicemia in Denmark, 1982–1995: review of 39 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 23, 71–75 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

