Standardized extract of Ficus deltoidea stimulates insulin secretion and blocks hepatic glucose production by regulating the expression of glucose-metabolic genes in streptozitocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 24993916
- PMCID: PMC4094436
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-220
Standardized extract of Ficus deltoidea stimulates insulin secretion and blocks hepatic glucose production by regulating the expression of glucose-metabolic genes in streptozitocin-induced diabetic rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Standardized extract of Ficus deltoidea stimulates insulin secretion and blocks hepatic glucose production by regulating the expression of glucose-metabolic genes in streptozitocin-induced diabetic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Sep 27;18(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2333-3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30261874 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Recently, there has been increasing interest in Ficus deltoidea Jack. (Moraceae) due to its chemical composition and the potential health benefits. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of extracts of F. deltoidea leaves on diabetes.
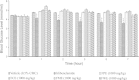
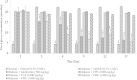
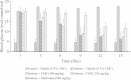
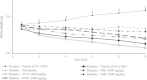
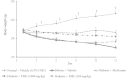
Methods: The petroleum ether, chloroform and methanol extracts of F. deltoidea were prepared and subjected to standardization using preliminary phytochemical and HPLC analysis. Dose selection was made on the basis of acute oral toxicity study (50-5000 mg/kg b. w.) as per OECD guidelines. Diabetes mellitus was induced with streptozotocin and rats found diabetic were orally administered with the extract (250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg) for 14 days. Levels of blood glucose and insulin were measured in control as well as diabetic rats on 0, 7 and 14th day. In addition, glucose metabolism regulating gene expression was assessed using RT-PCR.
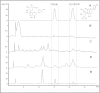
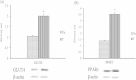
Results: HPLC analysis revealed that the methanol extract is enriched with C-glycosylflavones particularly, vitexin and isovitexin. In oral glucose tolerance test, oral administration of the methanol extract increased the glucose tolerance. The methanol extract showed significant (P < 0.01) antidiabetic activity. The extract treatment caused significant reduction (p < 0.01) in elevated fasting blood glucose level in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The streptozotocin-related weight loss in rats was noticeably reversed by the extract treatment. Finally, RT-PCR analysis revealed a novel mechanisms for the anti-diabetic action of methanol extract of F. deltoidea. The extract exerted its effect via an increase of insulin secretion which impeded the hepatic glucose production, via down-regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase genes expression on one hand, and up-regulation of hepatic GK and PPARγ genes expression on the other hand. The extract caused an increased expression of GLUT-4 gene expression in skeletal muscles which leads to normalize the hyperglycemia. The extract also nullified the toxic effects of streptozitocin by blocking its entry into the islet β-cells through reducing the expression of GLUT-2 gene.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that, F. deltoidea could potentially inhibits the streptozitocin-induced hyperglycemia in rats. Further the herb can be utilized as useful remedy for alleviation of diabetes complications.
Figures


References
-
- Eliza J, Daisy P, Ignacimuthu S, Duraipandiyan V. Antidiabetic and antilipidemic effect of eremanthin from Costus speciosus (Koen.) Sm., in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;182(1):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Rose AJ, Richter EA. Skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise: how is it regulated? Physiology. 2005;20(4):260–270. - PubMed
-
- Postic C, Dentin R, Girard J. Role of the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis. Diabetes Metabol. 2004;30(5):398–408. - PubMed
-
- Engström L. The regulation of liver pyruvate kinase by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;13:28–51. - PubMed
-
- Granner D, Pilkis S. The genes of hepatic glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(18):10173–10176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

