Loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction in mice prevents significant bone loss following ovariectomy
- PMID: 24994594
- PMCID: PMC4149851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.06.013
Loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction in mice prevents significant bone loss following ovariectomy
Abstract
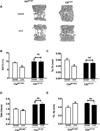
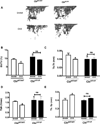
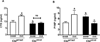
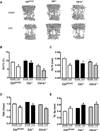
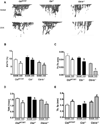
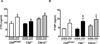
Cbl and Cbl-b are E3 ubiquitin ligases and adaptor proteins, which perform regulatory roles in bone remodeling. Cbl-/- mice have delayed bone development due to decreased osteoclast migration. Cbl-b-/- mice are osteopenic due to increased bone resorbing activity of osteoclasts. Unique to Cbl, but not present in Cbl-b, is tyrosine 737 in the YEAM motif, which upon phosphorylation provides a binding site for the regulatory p85 subunit of PI3K. Substitution of tyrosine 737 with phenylalanine (Y737F, CblYF/YF mice) prevents Y737 phosphorylation and abrogates the Cbl-PI3K interaction. We have previously reported that CblYF/YF mice had increased bone volume due to defective bone resorption and increased bone formation. Here we show that the lumbar vertebra from CblYF/YF mice did not have significant bone loss following ovariectomy. Our data also suggests that abrogation of Cbl-PI3K interaction in mice results in the loss of coupling between bone resorption and formation, since ovariectomized CblYF/YF mice did not show significant changes in serum levels of c-terminal telopeptide (CTX), whereas the serum levels of pro-collagen type-1 amino-terminal pro-peptide (P1NP) were decreased. In contrast, following ovariectomy, Cbl-/- and Cbl-b-/- mice showed significant bone loss in the tibiae and L2 vertebrae, concomitant with increased serum CTX and P1NP levels. These data indicate that while lack of Cbl or Cbl-b distinctly affects bone remodeling, only the loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction protects mice from significant bone loss following ovariectomy.
Keywords: Bone resorption; Cbl; Cbl-b; Osteoclast; Ovariectomy; PI3K.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Turner RT. Mice, estrogen, and postmenopausal osteoporosis. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 1999;14:187–191. - PubMed
-
- Swaminathan G, Tsygankov AY. The Cbl family proteins: ring leaders in regulation of cell signaling. Journal of cellular physiology. 2006;209:21–43. - PubMed
-
- Thien CBF, Langdon WY. Cbl: many adaptations to regulate protein tyrosine kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001;2:294–305. - PubMed
-
- Naramura M, Jang I-K, Kole H, Huang F, Haines D, Gu H. c-Cbl and Cbl-b regulate T cell responsiveness by promoting ligand-induced TCR down-modulation. Nature immunology. 2002;3:1192–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

