Natural epigenetic polymorphisms lead to intraspecific variation in Arabidopsis gene imprinting
- PMID: 24994762
- PMCID: PMC4115658
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03198
Natural epigenetic polymorphisms lead to intraspecific variation in Arabidopsis gene imprinting
Erratum in
-
Correction: Natural epigenetic polymorphisms lead to intraspecific variation in Arabidopsis gene imprinting.Elife. 2015 May 18;4:e08658. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08658. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25985306 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Imprinted gene expression occurs during seed development in plants and is associated with differential DNA methylation of parental alleles, particularly at proximal transposable elements (TEs). Imprinting variability could contribute to observed parent-of-origin effects on seed development. We investigated intraspecific variation in imprinting, coupled with analysis of DNA methylation and small RNAs, among three Arabidopsis strains with diverse seed phenotypes. The majority of imprinted genes were parentally biased in the same manner among all strains. However, we identified several examples of allele-specific imprinting correlated with intraspecific epigenetic variation at a TE. We successfully predicted imprinting in additional strains based on methylation variability. We conclude that there is standing variation in imprinting even in recently diverged genotypes due to intraspecific epiallelic variation. Our data demonstrate that epiallelic variation and genomic imprinting intersect to produce novel gene expression patterns in seeds.
Keywords: DNA methylation; epialleles; genomic imprinting; natural variation; seeds; transposable elements.
Copyright © 2014, Pignatta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



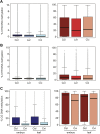
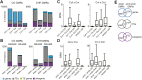

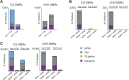
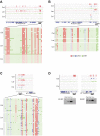
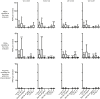
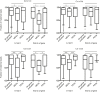


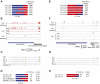

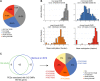
Comment in
-
DNA methylation: Switching phenotypes with epialleles.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Sep;15(9):572. doi: 10.1038/nrg3797. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25069489 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alonso-Blanco C, Blankestijn-De Vries H, Hanhart CJ, Koornneef M. Natural allelic variation at seed size loci in relation to other life history traits of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96:4710–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belmonte MF, Kirkbride RC, Stone SL, Pelletier JM, Bui AQ, Yeung EC, Hashimoto M, Fei J, Harada CM, Munoz MD, Le BH, Drews GN, Brady SM, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ. Comprehensive developmental profiles of gene activity in regions and subregions of the Arabidopsis seed. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110:E435–E444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222061110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

