Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties
- PMID: 24994950
- PMCID: PMC4074873
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-247
Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties
Abstract
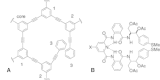
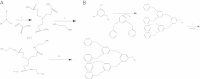
Dendrimers are nano-sized, radially symmetric molecules with well-defined, homogeneous, and monodisperse structure that has a typically symmetric core, an inner shell, and an outer shell. Their three traditional macromolecular architectural classes are broadly recognized to generate rather polydisperse products of different molecular weights. A variety of dendrimers exist, and each has biological properties such as polyvalency, self-assembling, electrostatic interactions, chemical stability, low cytotoxicity, and solubility. These varied characteristics make dendrimers a good choice in the medical field, and this review covers their diverse applications.
Keywords: Dendrimer; Nanoscale; PAMAM; Pseudorotaxane.
Figures

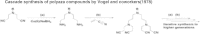


References
-
- Srinivasa-Gopalan S, Yarema KJ. Nanotechnologies for the Life Sciences: Dendrimers in Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis, Volume 7. New York: Wiley; 2007.
-
- Klajnert B, Bryszewska M. Dendrimers: properties and applications. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;9:199–208. - PubMed
-
- Tomalia DA, Frechet JMJ. Discovery of dendrimers and dendritic polymers: a brief historical perspective. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 2002;9:2719–2728.
-
- Tomalia DA. The dendritic state. Mater Today. 2005;9:34–36.
-
- Tomalia DA, Baker H, Dewald J, Hall M, Kallos M, Martin S, Roeck J, Ryder J, Smith P. A new class of polymers: starburst-dendritic macromolecules. Polym J (Tokyo) 1985;9:117.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

