Brain networks of perceptual decision-making: an fMRI ALE meta-analysis
- PMID: 24994979
- PMCID: PMC4063192
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00445
Brain networks of perceptual decision-making: an fMRI ALE meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Brain networks of perceptual decision-making: an fMRI ALE meta-analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Mar 22;11:139. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00139. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28337136 Free PMC article.
Abstract
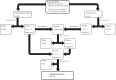
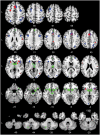
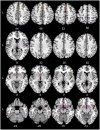
In the recent perceptual decision-making literature, a fronto-parietal network is typically reported to primarily represent the neural substrate of human perceptual decision-making. However, the view that only cortical areas are involved in perceptual decision-making has been challenged by several neurocomputational models which all argue that the basal ganglia play an essential role in perceptual decisions. To consolidate these different views, we conducted an Activation Likelihood Estimation (ALE) meta-analysis on the existing neuroimaging literature. The results argue in favor of the involvement of a frontal-parietal network in general perceptual decision-making that is possibly complemented by the basal ganglia, and modulated in substantial parts by task difficulty. In contrast, expectation of reward, an important aspect of many decision-making processes, shows almost no overlap with the general perceptual decision-making network.
Keywords: decision-making; fronto-parietal-basal ganglia; meta-analysis.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

