Peripheral injection of SB203580 inhibits the inflammatory-dependent synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in the hypothalamus
- PMID: 24995301
- PMCID: PMC4065737
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/475152
Peripheral injection of SB203580 inhibits the inflammatory-dependent synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in the hypothalamus
Abstract
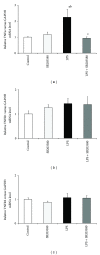
The study was designed to determine the effects of peripheral injection of SB203580 on the synthesis of interleukin- (IL-) 1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α in the hypothalamus of ewes during prolonged inflammation. Inflammation was induced by the administration of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (400 ng/kg) over 7 days. SB203580 is a selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), which is involved in the regulation of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα synthesis. Intravenous injection of SB203580 successfully inhibited (P < 0.01) synthesis of IL-1β and reduced (P < 0.01) the production of IL-6 in the hypothalamus. The p38 MAPK inhibitor decreased (P < 0.01) gene expression of TNFα but its effect was not observed at the level of TNFα protein synthesis. SB203580 also reduced (P < 0.01) LPS-stimulated IL-1 receptor type 1 gene expression. The conclusion that inhibition of p38 MAPK blocks LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine synthesis seems to initiate new perspectives in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases also within the central nervous system. However, potential proinflammatory effects of SB203580 treatment suggest that all therapies using p38 MAPK inhibitors should be introduced very carefully with analysis of all expected and unexpected consequences of treatment.
Figures



References
-
- Lawrence CB, Rothwell NJ. Anorexic but not pyrogenic actions of interleukin-1 are modulated by central melanocortin-3/4 receptors in the rat. Journal of Neuroendocrinology. 2001;13(6):490–495. - PubMed
-
- Herman AP, Tomaszewska-Zaremba D. Effect of endotoxin on the expression of GnRH and GnRHR genes in the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland of anestrous ewes. Animal Reproduction Science. 2010;120(1–4):105–111. - PubMed
-
- Ebisui O, Fukata J, Tominaga T, et al. Roles of interleukin-1α and -1β in endotoxin-induced suppression of plasma gonadotropin levels in rats. Endocrinology. 1992;130(6):3307–3313. - PubMed
-
- Palomba M, Bentivoglio M. Chronic inflammation affects the photic response of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Journal of Neuroimmunology. 2008;193(1-2):24–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

