Serum biomarkers for detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24995714
- PMCID: PMC4317379
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.23842
Serum biomarkers for detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Detection of hypermethylated circulating tumor DNA has the potential to be a minimally invasive, low cost, and reproducible method for cancer detection.
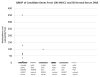
Methods: We evaluated serum from 100 patients with known head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and 50 healthy control patients for 3 previously described methylation targets, endothelin receptor type B (EDNRB), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A or p16), and deleted in colorectal carcinoma (DCC), using quantitative methylation specific polymerase chain reaction (qMSPCR).
Results: EDNRB hypermethylation was identified in the serum of 10% of the patients with HNSCC but in none of the control patients. DCC hypermethylation was detected in 2 serum samples from patients with cancer that also amplified EDNRB and one of these samples also had p16 hypermethylation. EDNRB hypermethylation was statistically significant by Fisher's exact test (p = .03) when comparing HNSCC to controls.
Conclusions: Serum EDNRB hypermethylation is a highly specific but not sensitive serum biomarker for HNSCC.
Keywords: epigenetics; head and neck cancer; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); hypermethylation; screening.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Belinsky SA, Liechty KC, Gentry FD, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in sputum precedes lung cancer incidence in a high-risk cohort. Cancer Res. 2006;66(6):3338–44. - PubMed
-
- Palmisano WA, Divine KK, Saccomanno G, et al. Predicting lung cancer by detecting aberrant promoter methylation in sputum. Cancer Res. 2000;60(21):5954–8. - PubMed
-
- Hoque MO, Begum S, Topaloglu O, et al. Quantitative detection of promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in the tumor, urine, and serum DNA of patients with renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64(15):5511–7. - PubMed
-
- Nunes DN, Kowalski LP, Simpson AJ. Detection of oral and oropharyngeal cancer by microsatellite analysis in mouth washes and lesion brushings. Oral Oncol. 2000;36(6):525–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous