The pros and cons of common actin labeling tools for visualizing actin dynamics during Drosophila oogenesis
- PMID: 24995797
- PMCID: PMC4438707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.06.022
The pros and cons of common actin labeling tools for visualizing actin dynamics during Drosophila oogenesis
Abstract
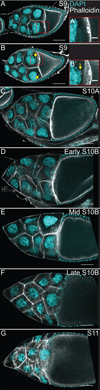
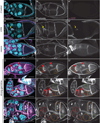
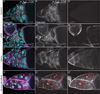
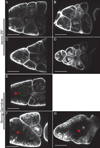
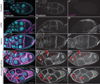
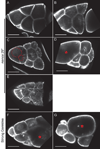
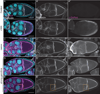
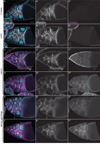
Dynamic remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton is required for both development and tissue homeostasis. While fixed image analysis has provided significant insight into such events, a complete understanding of cytoskeletal dynamics requires live imaging. Numerous tools for the live imaging of actin have been generated by fusing the actin-binding domain from an actin-interacting protein to a fluorescent protein. Here we comparatively assess the utility of three such tools--Utrophin, Lifeact, and F-tractin--for characterizing the actin remodeling events occurring within the germline-derived nurse cells during Drosophila mid-oogenesis or follicle development. Specifically, we used the UAS/GAL4 system to express these tools at different levels and in different cells, and analyzed these tools for effects on fertility, alterations in the actin cytoskeleton, and ability to label filamentous actin (F-actin) structures by both fixed and live imaging. While both Utrophin and Lifeact robustly label F-actin structures within the Drosophila germline, when strongly expressed they cause sterility and severe actin defects including cortical actin breakdown resulting in multi-nucleate nurse cells, early F-actin filament and aggregate formation during stage 9 (S9), and disorganized parallel actin filament bundles during stage 10B (S10B). However, by using a weaker germline GAL4 driver in combination with a higher temperature, Utrophin can label F-actin with minimal defects. Additionally, strong Utrophin expression within the germline causes F-actin formation in the nurse cell nuclei and germinal vesicle during mid-oogenesis. Similarly, Lifeact expression results in nuclear F-actin only within the germinal vesicle. F-tractin expresses at a lower level than the other two labeling tools, but labels cytoplasmic F-actin structures well without causing sterility or striking actin defects. Together these studies reveal how critical it is to evaluate the utility of each actin labeling tool within the tissue and cell type of interest in order to identify the tool that represents the best compromise between acceptable labeling and minimal disruption of the phenomenon being observed. In this case, we find that F-tractin, and perhaps Utrophin, when Utrophin expression levels are optimized to label efficiently without causing actin defects, can be used to study F-actin dynamics within the Drosophila nurse cells.
Keywords: Actin; Live Imaging; Oogenesis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prostaglandins temporally regulate cytoplasmic actin bundle formation during Drosophila oogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(3):397-411. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0366. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24284900 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of tools for live cell imaging of actin network architecture.Bioarchitecture. 2014;4(6):189-202. doi: 10.1080/19490992.2014.1047714. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Bioarchitecture. 2014. PMID: 26317264 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp60C is required in follicle as well as germline cells during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Dyn. 2008 May;237(5):1334-47. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21524. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18386820
-
Actin visualization at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2017 Feb 1;130(3):525-530. doi: 10.1242/jcs.189068. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28082420 Review.
-
The Vast Utility of Drosophila Oogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2626:1-36. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2970-3_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36715897 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear actin is a critical regulator of Drosophila female germline stem cell maintenance.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 28:2024.08.27.609996. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.27.609996. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253513 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A novel mechanism of bulk cytoplasmic transport by cortical dynein in Drosophila ovary.Elife. 2022 Feb 16;11:e75538. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75538. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35170428 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Fixation and Phalloidin Staining of Basally Localized F-Actin Networks in Collectively Migrating Follicle Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2626:179-191. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2970-3_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36715905 Free PMC article.
-
LILAC: enhanced actin imaging with an optogenetic Lifeact.Nat Methods. 2023 Feb;20(2):214-217. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01761-3. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 36717692 Free PMC article.
-
An endosome-associated actin network involved in directed apical plasma membrane growth.J Cell Biol. 2022 Mar 7;221(3):e202106124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202106124. Epub 2022 Jan 21. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35061016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image Processing with Image. J. Biophotonics International. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Aizawa H, Sameshima M, Yahara I. A green fluorescent protein-actin fusion protein dominantly inhibits cytokinesis, cell spreading, and locomotion in Dictyostelium. Cell structure and function. 1997;22:335–345. - PubMed
-
- Baarlink C, Wang H, Grosse R. Nuclear actin network assembly by formins regulates the SRF coactivator MAL. Science. 2013;340:864–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

