IRF4 is a key thermogenic transcriptional partner of PGC-1α
- PMID: 24995979
- PMCID: PMC4116691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.049
IRF4 is a key thermogenic transcriptional partner of PGC-1α
Abstract
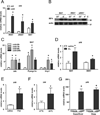
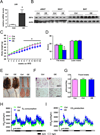
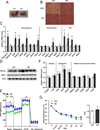
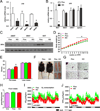
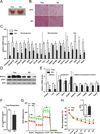
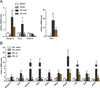
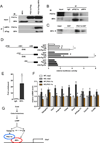
Brown fat can reduce obesity through the dissipation of calories as heat. Control of thermogenic gene expression occurs via the induction of various coactivators, most notably PGC-1α. In contrast, the transcription factor partner(s) of these cofactors are poorly described. Here, we identify interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) as a dominant transcriptional effector of thermogenesis. IRF4 is induced by cold and cAMP in adipocytes and is sufficient to promote increased thermogenic gene expression, energy expenditure, and cold tolerance. Conversely, knockout of IRF4 in UCP1(+) cells causes reduced thermogenic gene expression and energy expenditure, obesity, and cold intolerance. IRF4 also induces the expression of PGC-1α and PRDM16 and interacts with PGC-1α, driving Ucp1 expression. Finally, cold, β-agonists, or forced expression of PGC-1α are unable to cause thermogenic gene expression in the absence of IRF4. These studies establish IRF4 as a transcriptional driver of a program of thermogenic gene expression and energy expenditure.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nature reviews Genetics. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
-
- Brustle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplanter C, Stadelmann C, Yu P, Arpaia E, Mak TW, Kamradt T, Lohoff M. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nature immunology. 2007;8:958–966. - PubMed
-
- Cretney E, Xin A, Shi W, Minnich M, Masson F, Miasari M, Belz GT, Smyth GK, Busslinger M, Nutt SL, et al. The transcription factors Blimp-1 and IRF4 jointly control the differentiation and function of effector regulatory T cells. Nature immunology. 2011;12:304–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

