MRSA carriage among healthcare workers in non-outbreak settings in Europe and the United States: a systematic review
- PMID: 24996225
- PMCID: PMC4094410
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-363
MRSA carriage among healthcare workers in non-outbreak settings in Europe and the United States: a systematic review
Abstract
Abstarct background: A recent review estimated prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in healthcare workers (HCWs) to be 4.6%. However, MRSA carriage in HCWs in non-outbreak settings is thought to be higher than in an outbreak situation, due to increased hygiene awareness in outbreaks, but valid data are missing. The goals of this paper are to summarise the prevalence of MRSA carriage amongst HCWs in non-outbreak situations and to identify occupational groups in healthcare services associated with a higher risk of MRSA colonisation.
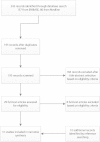
Methods: A systematic search for literature was conducted in the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases. The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using seven criteria. Pooled prevalence rates were calculated. Pooled effect estimates were identified in a meta-analysis.
Results: 31 studies were included in this review. The pooled MRSA colonisation rate was 1.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34%-2.50%). The rate increased to 4.4% (95% CI, 3.98%-4.88%) when one study from the Netherlands was excluded. The pooled MRSA rate was highest in nursing staff (6.9%). Nursing staff had an odds ratio of 1.72 (95% CI, 1.07-2.77) when compared with medical staff and an odds ratio of 2.58 (95%, 1.83-3.66) when compared with other healthcare staff. Seven studies were assessed as being of high quality. The pooled MRSA prevalence in high quality studies was 1.1% or 5.4% if the one large study from the Netherlands is not considered. The pooled prevalence in studies of moderate quality was 4.0%.
Conclusions: MRSA prevalence among HCWs in non-outbreak settings was no higher than carriage rates estimated for outbreaks. Our estimate is in the lower half of the range of the published MRSA rates in the endemic setting. Our findings demonstrate that nursing staff have an increased risk for MRSA colonisation. In order to confirm this finding, more studies are needed, including healthcare professionals with varying degrees of exposure to MRSA. In order to reduce misclassification bias, standardisation of HCWs screening is warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) related complications in surgical patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 19;2013(8):CD010268. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010268.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23959704 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carriage among the critical care personnel in a tertiary care hospital in Sikkim: An observational study.Indian J Med Res. 2025 Jan;161(1):91-98. doi: 10.25259/IJMR_1224_2024. Indian J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40036105 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):MR000034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000034.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 4;1:MR000034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000034.pub3. PMID: 24782322 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 21;7(7):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. PMID: 30030966 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage among health care workers at a Referral Hospital in Zabol, Iran.Pan Afr Med J. 2019 Dec 12;34:196. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2019.34.196.16645. eCollection 2019. Pan Afr Med J. 2019. PMID: 32180870 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic transmission of asymptomatic carriage Staphylococcus aureus on dairy farms in Canterbury, New Zealand.Microb Genom. 2024 Dec;10(12):001318. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001318. Microb Genom. 2024. PMID: 39630492 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Nasal Colonization by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Persons Using a Homeless Shelter in Kansas City.Front Public Health. 2016 Oct 25;4:234. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2016.00234. eCollection 2016. Front Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27826546 Free PMC article.
-
MRSA Prevalence and Risk Factors among Health Personnel and Residents in Nursing Homes in Hamburg, Germany - A Cross-Sectional Study.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 9;12(1):e0169425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169425. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28068356 Free PMC article.
-
MRSA Point Prevalence among Health Care Workers in German Rehabilitation Centers: A Multi-Center, Cross-Sectional Study in a Non-Outbreak Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 May 13;16(9):1660. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16091660. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31086069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Europe. Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) 2012. Stockholm: ECDC; 2013.
-
- NNIS. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) System Report, data summary from January 1992 through June 2004, issued October 2004. Am J Infect Control. 2004;14:470–485. - PubMed
-
- Gagliotti C, Balode A, Baquero F, Degener J, Grundmann H, Gur D, Jarlier V, Kahlmeter G, Monen J, Monnet DL, Rossolini GM, Suetens C, Weist K, Heuer O. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: bad news and good news from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net, formerly EARSS), 2002 to 2009. Euro Surveill. 2011;14:pii19819. - PubMed
-
- Acton DS, Plat-Sinnige MJ, van Wamel W, de Groot N, van Belkum A. Intestinal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: how does its frequency compare with that of nasal carriage and what is its clinical impact? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009;14:115–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical