Adjudication of etiology of acute kidney injury: experience from the TRIBE-AKI multi-center study
- PMID: 24996668
- PMCID: PMC4091753
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-105
Adjudication of etiology of acute kidney injury: experience from the TRIBE-AKI multi-center study
Abstract
Background: Adjudication of patient outcomes is a common practice in medical research and clinical trials. However minimal data exists on the adjudication process in the setting of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) as well as the ability to judge different etiologies (e.g. Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN), Pre-renal Azotemia (PRA)).
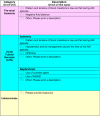
Methods: We enrolled 475 consecutive patients undergoing cardiac surgery at four sites of the Translational Research Investigating Biomarker Endpoints in AKI (TRIBE-AKI) study. Three expert nephrologists performed independent chart review, utilizing clinical variables and retrospective case report forms with pre intra and post-operative data, and then adjudicated all cases of AKI (n = 67). AKI was defined as a > 50% increase in serum creatinine for baseline (RIFLE Risk). We examined the patterns of AKI diagnoses made by the adjudication panel as well as association of these diagnoses with pre and postoperative kidney injury biomarkers.
Results: There was poor agreement across the panel of reviewers with their adjudicated diagnoses being independent of each other (Fleiss' Kappa = 0.046). Based on the agreement of the two out of three reviewers, ATN was the adjudicated diagnosis in 41 cases (61%) while PRA occurred in 13 (19%). Neither serum creatinine or any other biomarker of AKI (urine or serum), was associated with an adjudicated diagnosis of ATN within the first 24 post-operative hours.
Conclusion: The etiology of AKI after cardiac surgery is probably multi-factorial and pure forms of AKI etiologies, such as ATN and PRA may not exist. Biomarkers did not appear to correlate with the adjudicated etiology of AKI; however the lack of agreement among the adjudicators impacted these results.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00774137.
Figures
References
-
- Mangano CM, Diamondstone LS, Ramsay JG, Aggarwal A, Herskowitz A, Mangano DT. Renal dysfunction after myocardial revascularization: risk factors, adverse outcomes, and hospital resource utilization. The Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(3):194–203. - PubMed
-
- Tuttle KR, Worrall NK, Dahlstrom LR, Nandagopal R, Kausz AT, Davis CL. Predictors of ARF after cardiac surgical procedures. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41(1):76–83. - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Coca SG, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, Wang Z, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, Patel UD, Zappitelli M, Krawczeski CD, Passik CS, Swaminathan M, Garg AX. Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after adult cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(9):1748–1757. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Devarajan P, Zappitelli M, Sint K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Li S, Kim RW, Koyner JL, Coca SG, Edelstein CL, Shlipak MG, Garg AX, Krawczeski CD. Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(9):1737–1747. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004;8(4):R204–R212. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

